Gold Open Access Journal Focused on Head and Neck Surgery: Analysis of Business Model and Level of Article Processing Charges during the First 31 Months of Publishing
August 31, 2019
https://doi.org/10.23999/j.dtomp.2019.8.6
J Diagn Treat Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2019;8:202−12
Under a Creative Commons license
HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE
Fesenko II. Gold open access journal focused on head and neck surgery: analysis of business model and level of article processing charges during the first 31 months of publishing. J Diagn Treat Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2019;3(8):202−12.
INSTITUTIONAL REPOSITORY
https://ir.kmu.edu.ua/handle/123456789/728
Contents: Abstract | Introduction | Materials & Methods | Results | Discussion | References (22)
ABSTRACT
Purpose: The goal of this retrospective study was 1) to analyze the results of a gold open access (OA) business model on the example of 31-month-old journal Otolaryngology Case Reports (OCR) related with head neck surgery and 2) to understand ‘pro and contra’ of this business model.
Materials and Methods: Editorial board, publication history, indexation, and assumed revenue/profit margin were scrupulously investigated. We analyzed the data of articles` portfolio (which included 117 papers) of a gold OA journal focused on head neck surgery, the official journal’s and publisher`s website pages. The publication is analyzed from the first to the eleventh volume.
Results: The entire study showed that during 2 years and 7 months of OCR existence totally 117 case report articles have been published. The assumed revenue reached 83,550 US dollars (mean revenue, USD 2,695.16 per month) and profit margin is 30,913.50 US dollars (a 37% profit margin was used upon calculation, as the official data reported by Elsevier`s for its OA products). The editorial board, abstracting and indexation are analyzed, and the 31-month publication history compared with a 33-month history of another gold OA journal Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Cases. Conclusions about 31-month OCR publishing results are presented.
Introduction
Before launching a new journal in the field of oral and maxillofacial surgery or head neck surgery the initiative team of editors or surgical community/institution has a great need to understand not only a scientific aspect of journal`s life but a financial one as well for it can be another key to successful existence and growth of a new publication. Five types of the financial-aspect proposals from publishers to the researchers can be found (Boukacem‐Zeghmouri et al,1 2018):
-
Closed journals2 with traditional subscription model (eg, Microsurgery).
-
Gold OA journals (eg, Otolaryngology Case Reports and Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Cases).
-
Platinum OA journals also termed gold OA publications that do not receive OA fees from authors (eg, International Journal of Implant Dentistry).
-
Gold hybrid journals: combination of toll-access and OA articles. Eg, 1) Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, and Oral Radiology, 2) Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Medicine, and Pathology, and 3) Journal of Diagnostics and Treatment of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology.
-
Delayed OA journals (eg, JAMA Otolaryngology–Head & Neck Surgery). In those types of journals, the articles became OA at the expiry of a set embargo period.2 Embargo period in JAMA Otolaryngology–Head & Neck Surgery for the research papers is 12 months.
Another OA model is a ‘green OA’. First, it's hard to understand its difference from gold one. But Elsevier`s describes its main features: 1) publishing costs are covered by library subscriptions and there is no fee for authors, and 2) time delay may be applied (synonym: embargo period).3 Laakso and Björk stated that gold and green OA models are not two opposite OA concepts; rather, gold OA plus delayed OA should be contrasted with green OA.2
So, the goal of our retrospective study was 1) to analyze the results of a gold OA business model on the example of 31-month-old journal related with head neck surgery and 2) to understand pro and contra of this business model.
MATERIALS & METHODS
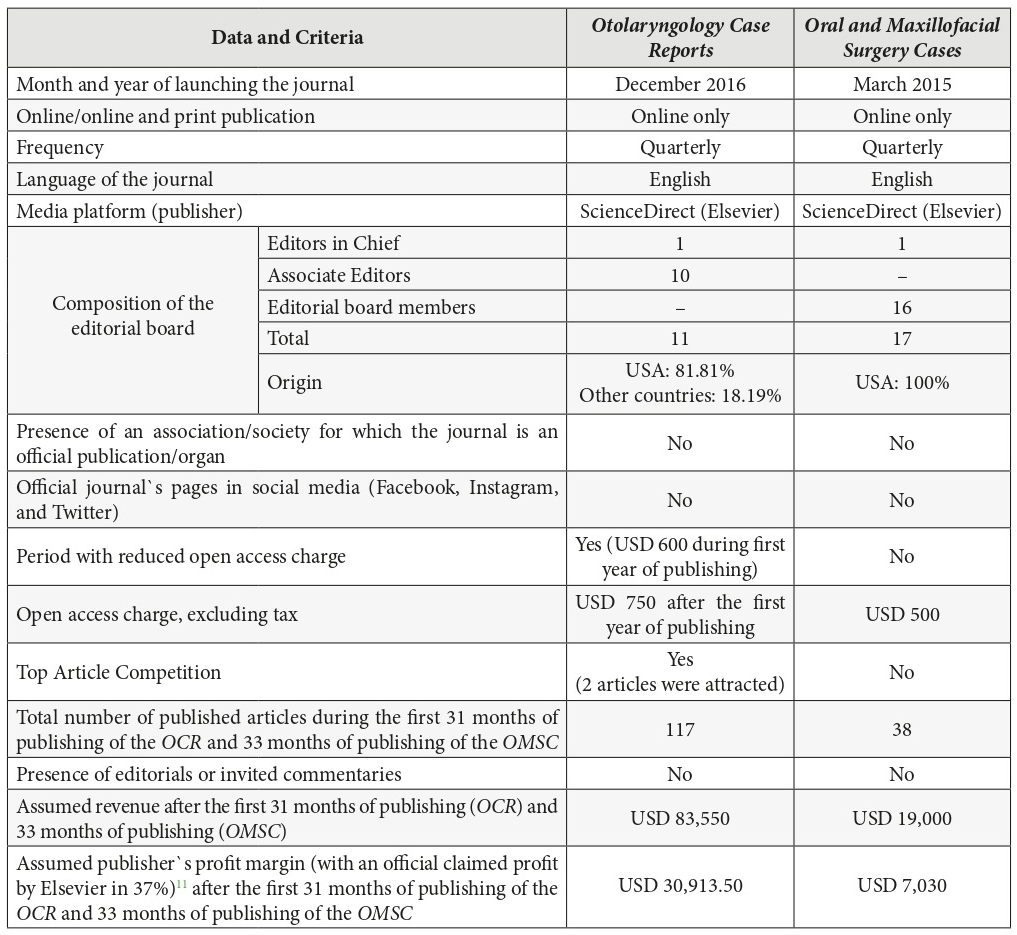
Editorial board, publication history, indexation, and assumed revenue/profit margin were scrupulously investigated. We analyzed the data of articles` portfolio (which included 117 papers) of gold open access journal Otolaryngology Case Reports (OCR) focused on head neck surgery, the official journal’s and publisher`s website pages. The OCR is analyzed from the first to the eleventh volume. Received data have been compared with publication history results of another gold OA journal Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Cases described in study of Robles Cantero et al.4
RESULTS
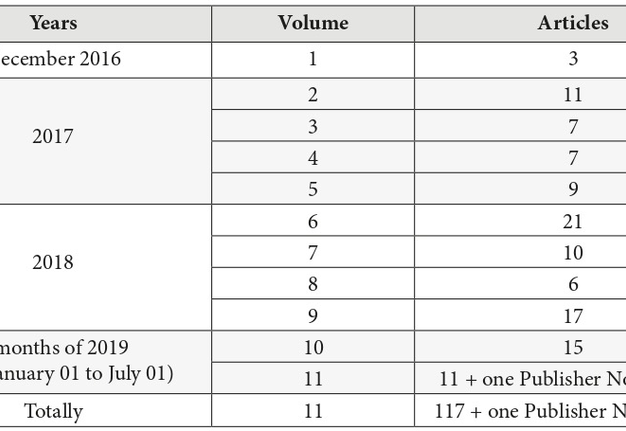
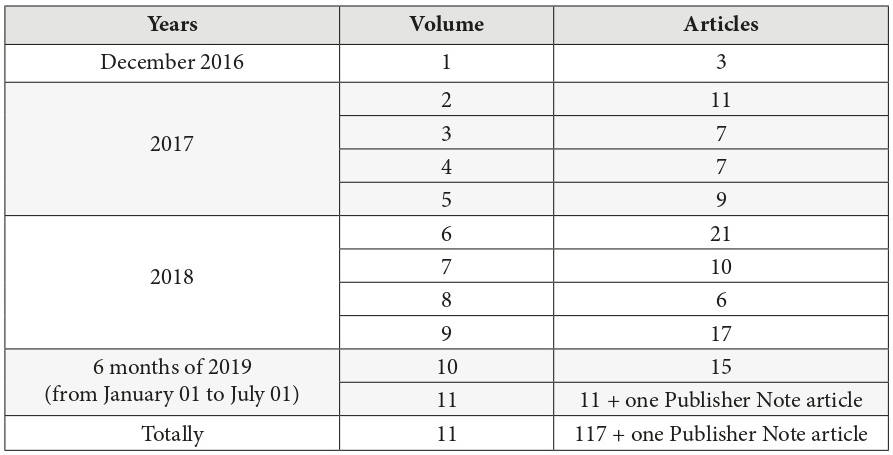
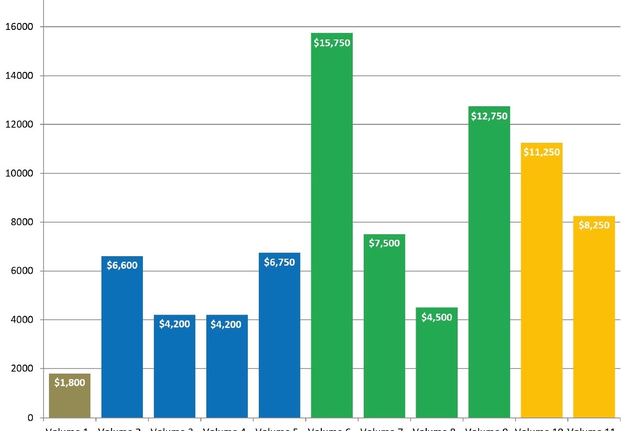
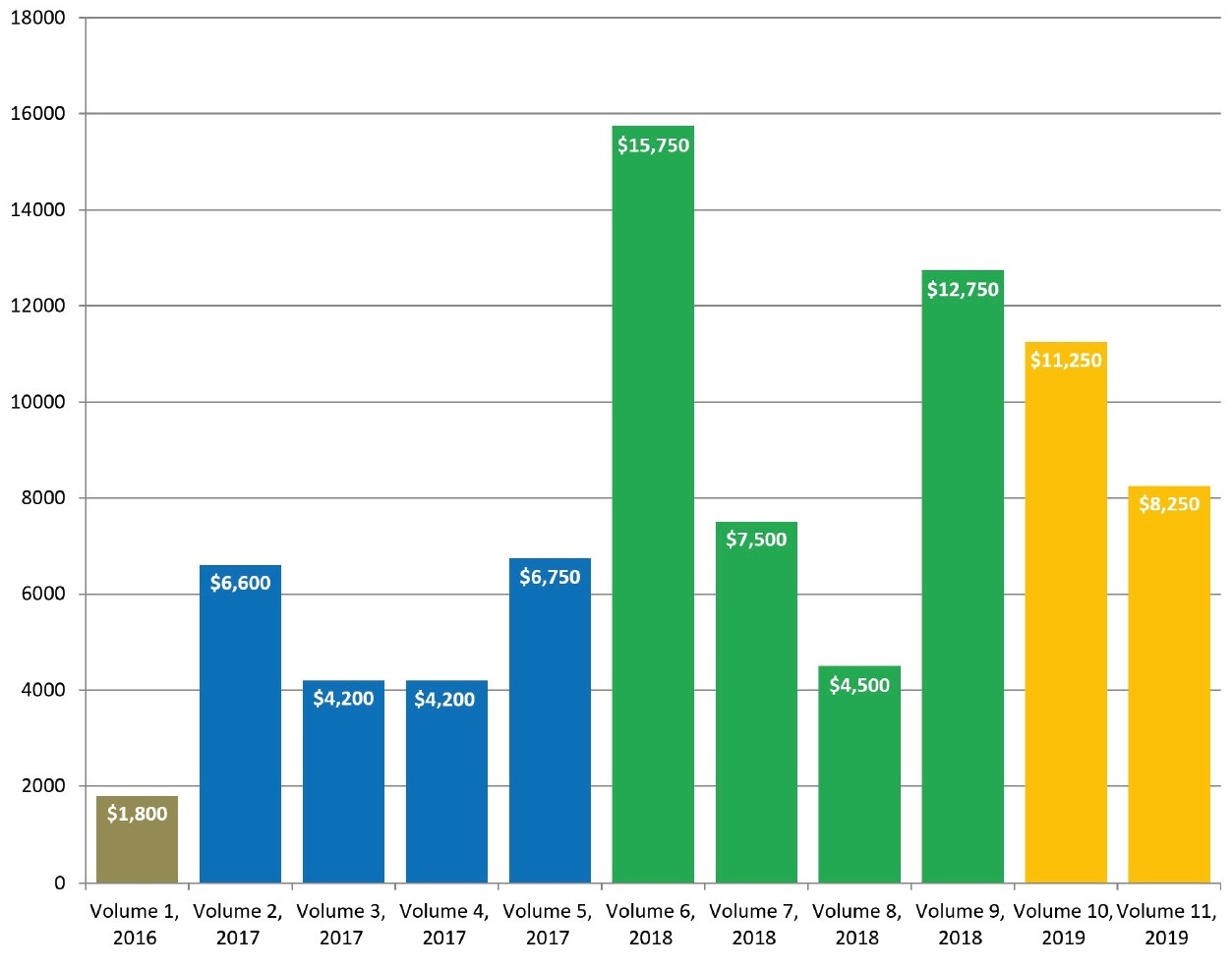
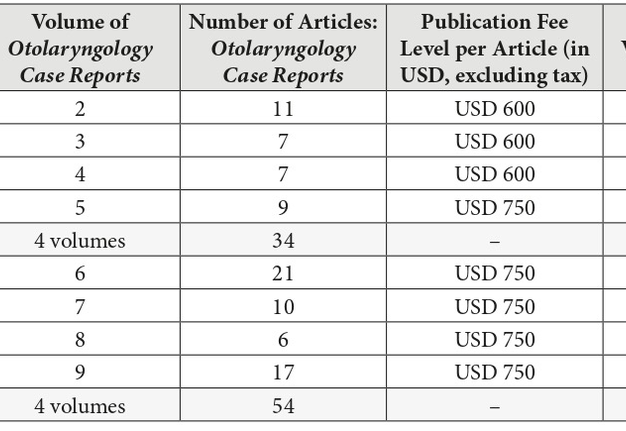
Otolaryngology Case Reports (OCR), which was launched in December 2016, belongs to the gold OA journals. The OCR is a quarterly online-only publication focusing on case reports in all sections of adult and pediatric otolaryngology.5, 6 In case of the OCR, the publisher avoids dividing published numbers into issues and volumes, and used only the term ‘volume’. During 2 years and 7 months of the OCR existence, 117 peer-reviewed papers have been published (mean, 10.6 articles per 1 volume) (Table 1). Comparing two full years of OCR publication, we obtain that 34 articles in 2017 have been published and 54 articles – in 2018 (Fig 1). This indicates about 59% submissions` growth in a second year of a full year OCR`s publishing. Among nine volumes, a sixth`s volume (ie, after 1 year and 6 months from launching) became the journal`s issue with a greatest number of published articles – 21.
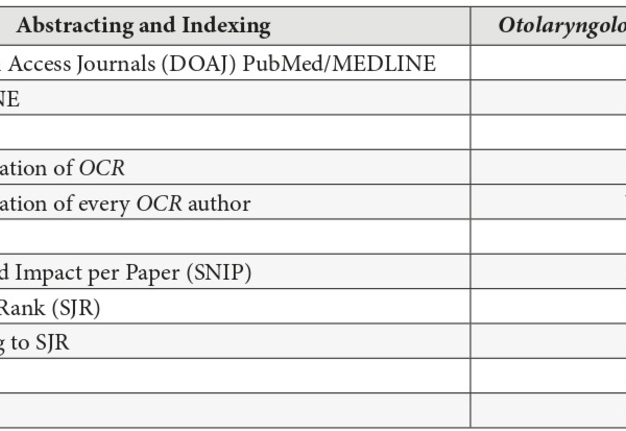
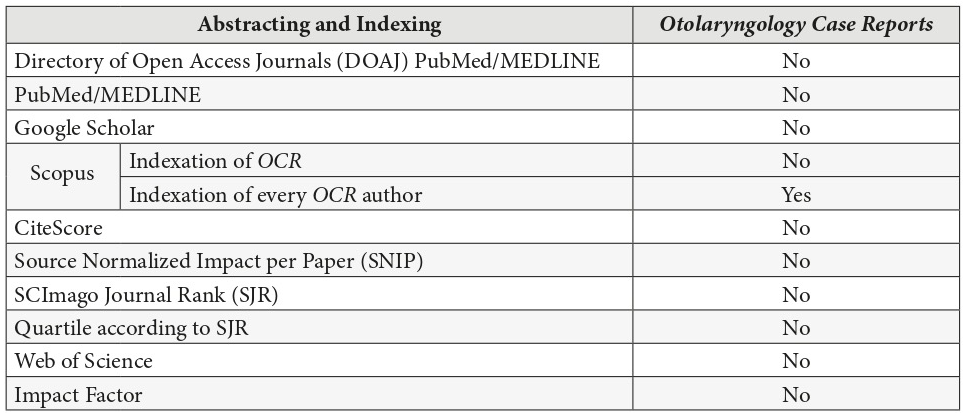
At moment of publishing of this article no information was found that the OSR journal is listed in the SCImago Journal and Country Rank website, which covers 109 journals which the subcategory ‘otorhinolaryngology’ in category ‘medicine’.7 It is officially stated, that the journal cannot be added to the SCImago Journal and Country Rank if it`s not included in Scopus database first.8 Despite the fact that we did not find any information that journal is covered by Scopus, every OSR`s author has a record in Scopus preview about each article published in OSR and in other journals. For example, an author John C. Simmons has two records in Scopus preview9: one about publication in OCR,9 another – in Laryngoscope.11 That record terms ‘author stats’ and the author is benefitted having access to a special dashboard with citation and usage data.6 “This free service is available to anyone who has published and whose publication is in Scopus,” is stated at the official journal`s page.6 From that phrase we can conclude that every article published in the OCR is indexed by Scopus. Nevertheless, to the question “Is this journal indexed in Scopus?” the SCImago Journal and Country Rank website gives an official answer: “All journals included in SJR are indexed in Scopus. Elsevier/Scopus is our data provider, so we cannot add any journal that is not included in Scopus data base.”8 That is why we concluded that OCR is not covered by Scopus in general as we did not found the journal’s name in the list of 109 journals.7 So, at the moment of submission of our manuscript to publication, the OCR does not have a possibility to be included to SCImago Journal and Country Rank and to receive CiteScore, Source Normalized Impact per Paper (SNIP), and to take a certain quartile (Fig 2) as it`s not indexed by Scopus.6 The situation when every OCR author and his/her publication are indexed by Scopus, but the journal in general is not, looks a bit ambiguous but we report the official data.
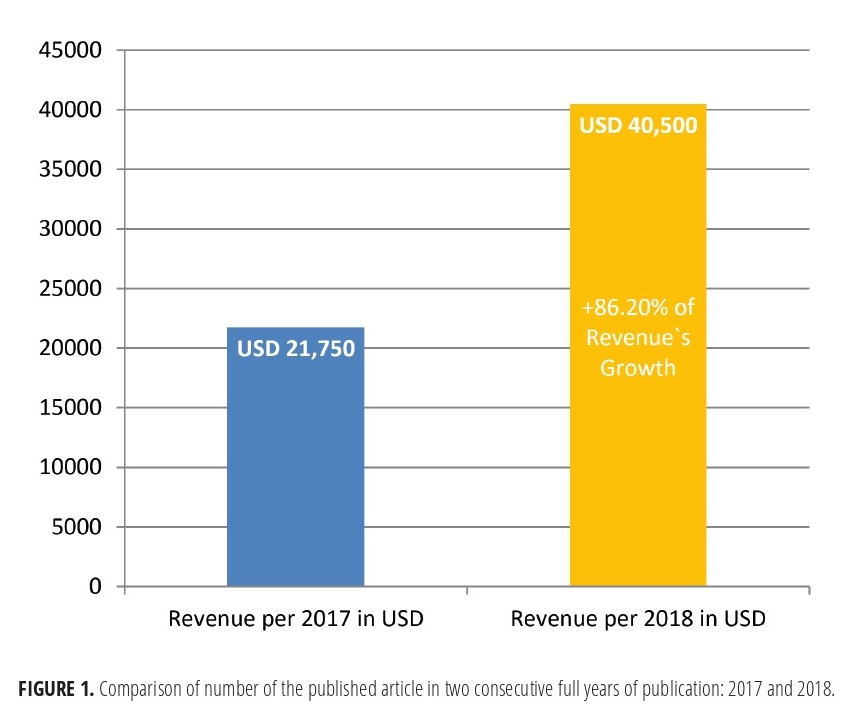
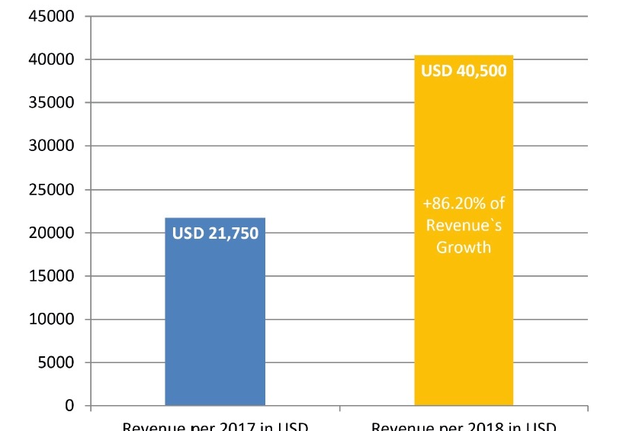
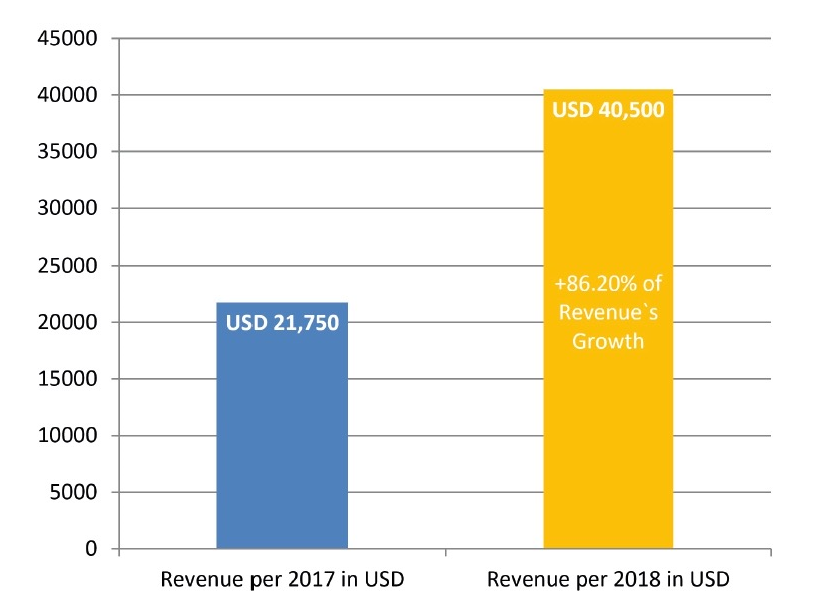
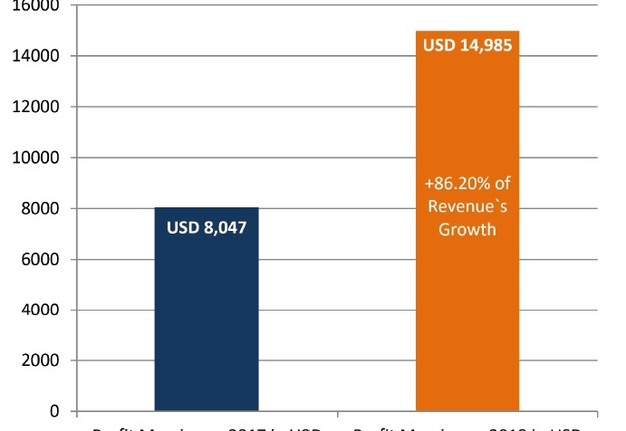
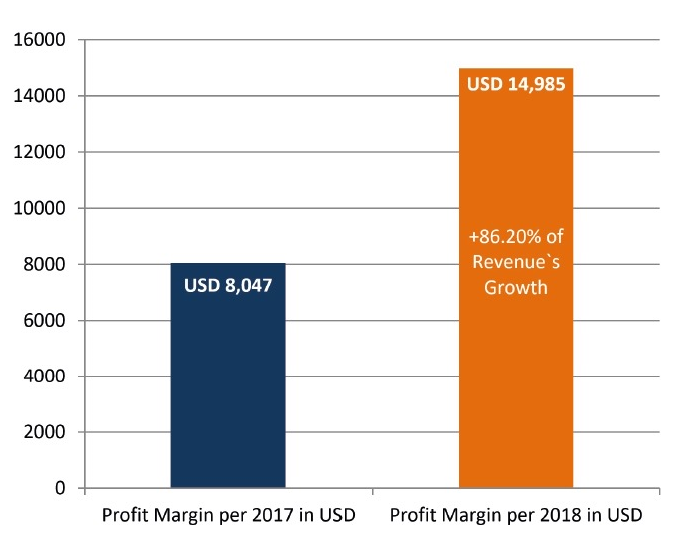
FIGURE 3. Comparing of estimated revenue and its growth during the first two full years of publishing. The term full year of publishing is used to describe a year in which all 4 volumes were published. Note, that as in the launching year 2016 only one volume (December) was published we took 2016 as ‘not-full year of publishing’.
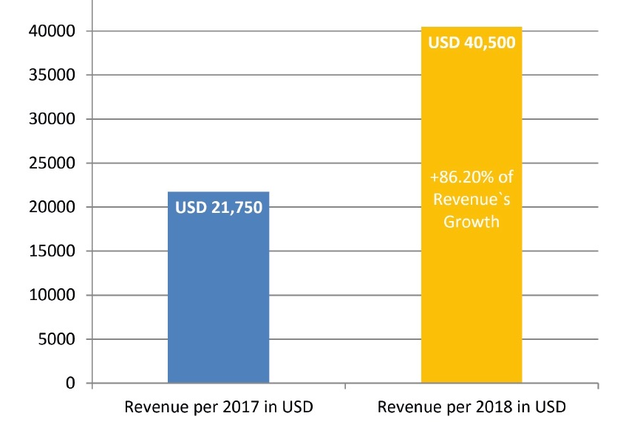
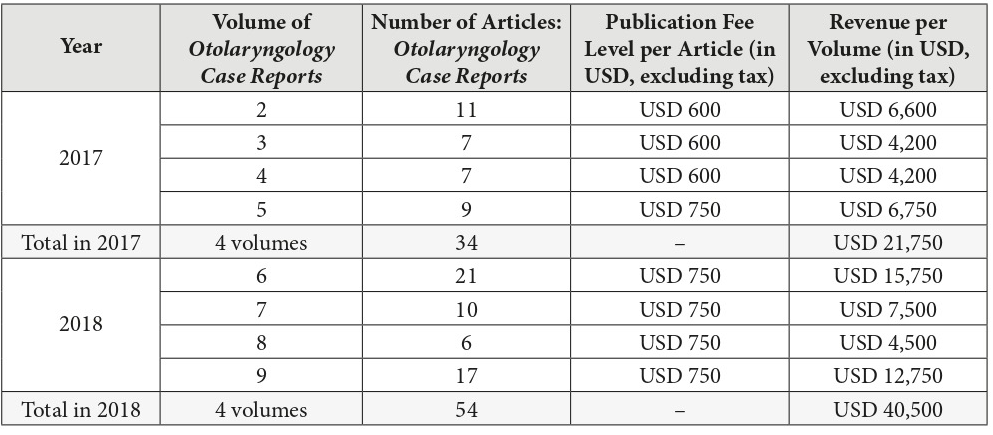
In the first twelve months of publishing (from volume 1 [December 2016] to volume 4 [September 2017]), the article processing charge (APC) was discounted to USD 600 and from December 2017 became USD 750, excluding taxes.5 So, in case of Elsevier`s indicated level of fee in OSC,6 we can assume that publisher`s revenue during thirty-one months of the publication of 117 articles (Table 1) reached USD 83,550 excluding taxes. Comparison of assumed revenue of different volumes from the moment of launching the journal is presented in Fig 2. Taking into account the data of Van Noorden (2013)12 that Elsevier`s reported profit margin is 37 percent, the calculated the margin from US$83,550 (mean revenue, USD 2,695.16 per month) is 30,913.50 US dollars in 2 years and 7 months. Revenue of the first full year of publishing (2017), was assumed in amount of USD 21,750 (Table 3). We used the term full year of publishing to describe a year in which all 4 volumes have been published. When the single volume (December) was published, we indicated a year 2016 as not-full year of publishing). Mean profit margin in 2017 (upon calculation we used a 37% profit margin, as officially reported data by Elsevier`s for its OA products) reached USD 8,047.50.
Revenue of a second full year of publishing (2018) we astimated in amount of USD 40,500 (Table 3 and Fig 3). Mean profit margin in 2017 (upon calculation we used a 37% profit margin, as officially reported data by Elsevier`s for its OA products) allegedly reached USD 14,985. This clearly demonstrates 86.20 percent revenue`s and profit margin`s growth in the second full year of publication.
To encourage the authors, the publisher gives a possibility for the winners of a special nomination ‘Top Article Competition’13 to get open access fee waiver for the future submission to the Otolaryngology Case Reports.7, 14 The winners were two collectives of authors in the period from September 1, 2017 to February 1, 2018.
DISCUSSION
Green in 2019 has concluded that over the seven-year period 2010–2016, the number of new open access publications launched averaged 870 titles per year, and launches further increased in 2016.15 This statistics and tendency cannot be ignored by publishers and editorial teams before launching a new journal as it indicates a new wide range of possibilities: 1) for readers – to read without payments, 2) for authors – to receive a higher citation rate of their works, and 3) for publishers – to receive income immediately. Among different OA business models,1 the gold open access journal4 is one of the most popular.16 Despite the fact that green open access journals prevail,16 in 2016 the number of published green and gold OA articles almost equalized (according to the European Commission Open Science Monitor calculations using Scopus database).15 Analysis of a 2.5-year publishing history of gold open-access publication focused on head neck surgery cases gave us an example what number of attracted articles, estimated revenue and profit margin can be reached in case of the OCR journal’s conditions.
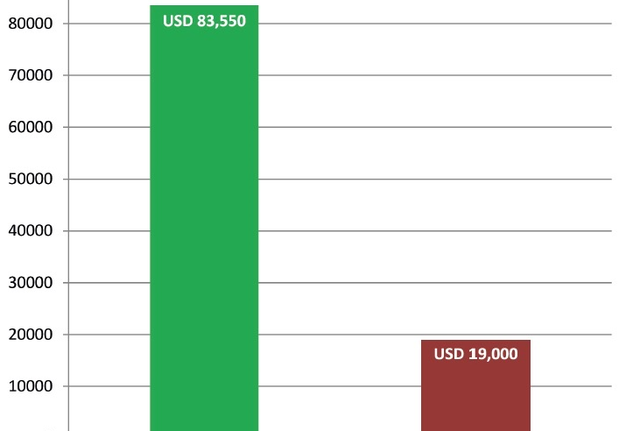
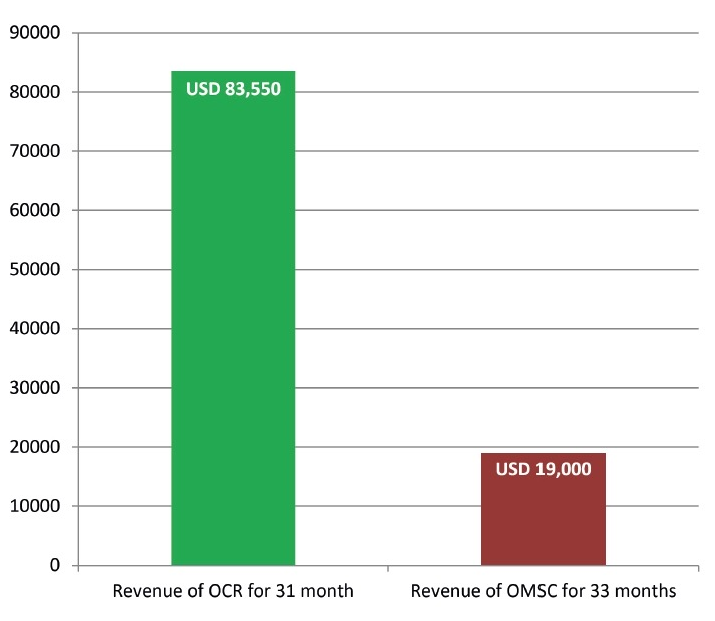
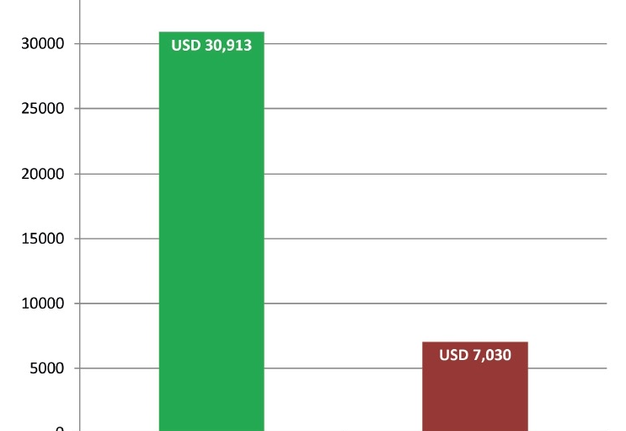
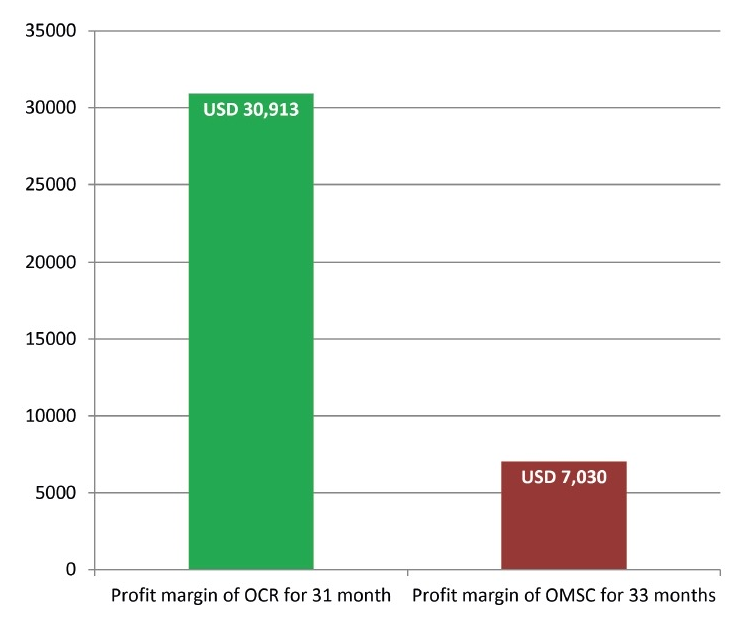
Despite the fact that the OCR’s editorial board is 6 persons less (Table 4) than the editorial board of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Cases journal (17 persons in editorial board),17, 4 the OCR during first 31 month published 117 papers comparing to total 38 articles of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Cases (OMSC) during first 33 months. This is confirmed by the 3.07 times higher result of OCR journal in number of published manuscripts. And that, in turn, transforms into significantly greater revenue (estimated revenue after 31 month of OCR is USD 83,550 [Table 4 and Fig 5] and revenue after 33 month of publishing of the OMSC is USD 19,000 [an official journal`s OA fee in amount of USD 500 was used for calculation]18). The OMSC assumed profit margin is USD 7,030 after 33 months of publication (Fig 6).
One of the main differences in the editorial board of two journals is that OCR has 10 associate editors and no editorial board members. Despite the fact that exact role of the associate editor varies from journal to journal,19 a Spinal Cord Nature journal defines the functions of the associate editor as follows: “To make initial decisions about suitability for review and then allocate reviewers and make a final recommendation as to whether a paper is suitable for publication.”20 For example, Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery (print and online publication of Elsevier) has only 1 associate editor position, 11 editorial board members, and 12 international editorial board members; 21 Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery–Global Open (online only publication of Wolters Kluwer) has 124 associate editors and doesn’t have editorial board members.22 The overwhelming number of associate editors with broader functions and responsibilities could theoretically result in higher quantity of attracted and published articles. Unfortunately, no information was found about acceptance rate in both journals, OCR and OMSC. The role of the association/society in encouraging the submission of manuscripts may be completely excluded, as no information about such community was found in case of OCR and OMSC (Table 4). As OCR is not covered by PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, and doesn’t have an impact factor, it`s impossible to think that these abstracting and indexing databases played some role in attraction the authors of 117 articles. The same can be concluded about absence of official OCR pages in Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter.
According to our opinion, such type of motivational competition as ‘Top Article Competition’13 is a useful possibility to attract new authors, to reward those committed, and to expend portfolio of articles. Also, reducing APC to 600 US dollars during the first year can theoretically attract some authors. High world reputation of Elsevier as a publisher, quality of ScienceDirect media platform where journal is based, and authority of the editorial board cannot be ignored when understanding all ways to attract new authors.
From the results of our study we estimated the effectiveness of gold open access business model of the journal focused on head neck surgery during first 2.5-year from launching the online-only journal based on:
-
Precise amount of attracted articles in first and second full years of publishing with a level of OAC in amount of USD 600 (excluding tax) during first full year and USD 750 (excluding tax) during second year.
-
Calculation the estimated revenue and profit margin during each year based on the official information of the publisher.
From the obtained results, a prognostic information is derived for calculation a possible future results and growth’s tendencies when planning a launch of new journal with similar conditions.
REFERENCES (22)
-
Boukacem‐Zeghmouri C, Dillaerts H, Lafouge T, Bador P, Sauer‐Avargues A. French publishing attitudes in the open access era: the case of mathematics, biology, and computer science. Learn Publ 2018;31:345–54. Crossref
-
Laakso M, Björk B. Delayed open access: an overlooked high‐impact category of openly available scientific literature. J Am Soc Inf Sci Tec 2013;64:1323–9. Crossref
-
Elsevier: Open access [document on the internet]; 2019 [cited 2019 Jul 31]. Available from: https://www.elsevier.com/about/open-science/open-access.
-
Robles Cantero D, Schoenbaum TR, Zhehulovych ZY, Nagorniak IV, Fesenko II. Comparison of article processing fees on open access journals with a 4.5-year history of publishing. J Diag Treat Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2019;3:176–82. Crossref
-
Otolaryngology Case Reports: news: launch of Otolaryngology Case Reports [document on the internet]; January 26, 2017 [cited 2019 Jul 26]. Available from: Link
-
Otolaryngology Case Reports [document on the internet]; 2019 [cited 2019 Jul 31]. Available from: Link
-
SCImago Journal & Country Rank: journal ranking: otorhinolaryngology [document on the internet]; 2019 [cited 2019 Aug 07]. Available from: Link
-
SCImago Journal Rank: help [document on the internet]; 2019 [cited 2019 Aug 07]. Available from: Link
-
Scopus preview: author details: Simmons, John C [document on the internet]; 2019 [cited 2019 Aug 02]. Available from: Link
-
Wall AE, Gelbard A, Vinh D, Simmons JC, Donovan DT, Grogan E, Ongkasuwan J. Management of laryngotracheal complications of inherited epidermolysis bullosa in the adult: a case series. Otolaryngol Case Rep 2018;6:14–5. Crossref
-
Gelbard A, Francis DO, Sandulache VC, Simmons JC, Donovan DT, Ongkasuwan J. Causes and consequences of adult laryngotracheal stenosis. Laryngoscope 2015;125:1137–43. Crossref
-
Van Noorden R. Open access: the true cost of science publishing. Nature 2013;495(7442):426–9. Crossref
-
Otolaryngology Case Reports: news: winners of Top Article Competition [document on the internet]; 2019 [cited 2019 Jul 27]. Available from:Link
-
Sousa LCA, Bellodi AJ, Braga DO, Pauna HF. Pyoderma gangrenosum after stapedotomy – first report in otolaryngology literature. Otolaryngol Case Rep 2018;6:22–4. Crossref
-
Green T. Is open access affordable? Why current models do not work and why we need internet‐era transformation of scholarly communications. Learn Publ 2019;32:13–25. Crossref
-
Mukherjee B. Green and gold open access in India. Learn Publ 2014;27:21–32. Link
-
Otolaryngology Case Reports: editorial board [document on the internet]; 2019 [cited 2019 Jul 27]. Available from: Link
-
Elsevier: browse journals: Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Cases: open access journal [document on the internet]; 2019 [cited 2019 Aug 19]. Available from: Link
-
Wiley: editors: editorial office guidelines: editorial board [document on the internet]; 2019 [cited 2019 Aug 21]. Available from: Link
-
Harvey LA. Introducing our new associate editors and editorial board members. Spinal Cord 2017;55:525. Crossref
-
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery: journal info: editorial board [document on the internet]; 2019 [cited 2019 Aug 21]. Available from: Link
-
Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery–Global Open: home: editorial board [document on the internet]; 2019 [cited 2019 Aug 21]. Available from: Link