Impact of Surgeon’s Instagram Television (IGTV): A Case of Chimeric Fibula and Soleus Muscle Transplant in a Reconstruction of Cordeiro Type IIIA Total Maxillectomy Defect
January 31, 2020
https://doi.org/10.23999/j.dtomp.2020.1.1
J Diagn Treat Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2019;4:3−20.
Under a Creative Commons license
HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE
Massarelli O, Hanna TC, Ganry L, Nagorniak IV, Fesenko II. Impact of surgeon`s Instagram television (IGTV): a case of chimeric fibula and soleus muscle transplant in a reconstruction of Cordeiro type IIIA total maxillectomy defect. J Diagn Treat Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2020;4(1):3–20.
INSTITUTIONAL REPOSITORY
https://ir.kmu.edu.ua/handle/123456789/720
Contents: Introduction | IGTV Chimeric Flap Case | IGTV Statistics of the Case | Discussion | Conclusions | Patient Consent | References (28)
It`s time for videos to move forward and evolve.
—Kevin Systrom
Co-founded Instagram and launched IGTV
Introduction
IGTV, a new option provided by Instagram Inc., was launched in June 20, 2018, i.e. 7 years 8 months after starting parent application–social media.1 IGTV is both a standalone application and available within an Instagram but only in basic functionality. Four letters of the acronym “IGTV” mean “Instagram Television.”2 Lydia Belanger also described IGTV as a “social-media based television” and “Instagram`s new longform video app.”3
Meanwhile, multiple advantageous role of the chimeric flaps in a jaw reconstructive surgeries continues to increase during last three decades.4, 5, 6 Fibula free flap,7 being alone an extremely productive workhorse in all types of jaw reconstructions8 including “jaw-in-a-day surgery,”9 can also be successfully used with soleus muscle in a chimeric manner for composite defect reconstructions.10, 11
Combination of the social media`s (in our particular case it is Instagram) advantages with IGTV (i.e., a longform video application), and a professional quality recording system12 can perfectly highlight the operation and bring the surgical tips and tricks from operating room to the internet environment with more than 1 billion users.13 The purpose of our editorial is to describe an educational IGTV microvascular surgery video case from both technological and surgical aspect.
IGTV CHIMERIC FLAP CASE
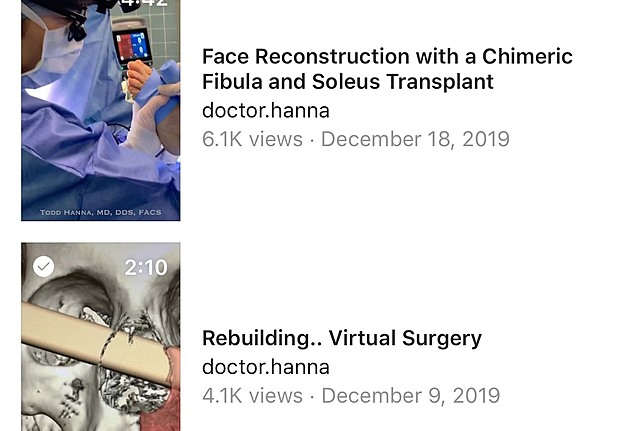
The IGTV video of the maxilla-reconstruction case with a title “Face reconstruction with a chimeric fibula and soleus transplant” was published by Dr. Hanna on December 18, 2019. It depicts an intraoperative look on 10 consecutive stages (named by the surgeon [T.C.H.] as “Chapters” to emphasize the educational purposes of this IGTV flap case) of the microvascular operation (it lasted 12 hours 9 minutes). A surgery was performed in operating room of a Private Surgical Practice in New York City, New York, United States. Duration of this IGTV video, illustrating a free fibula osteocutaneous flap with soleus muscle as a chimeric flap, reached 4 minutes 42 seconds, and it became a sixth video in an IGTV account of Dr. Hanna (@doctor.hanna).
The 10 steps of the surgery which were presented in the IGTV case are next ones:
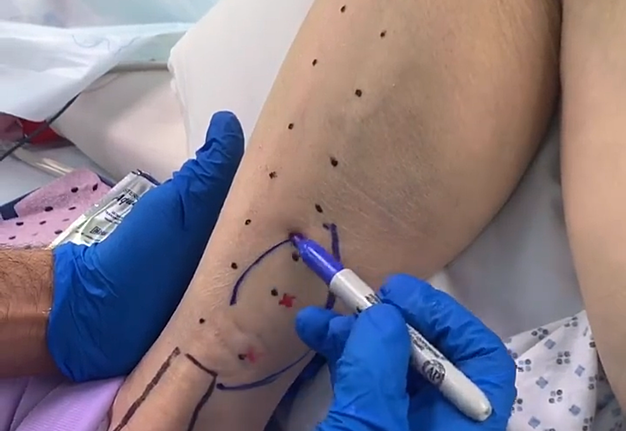
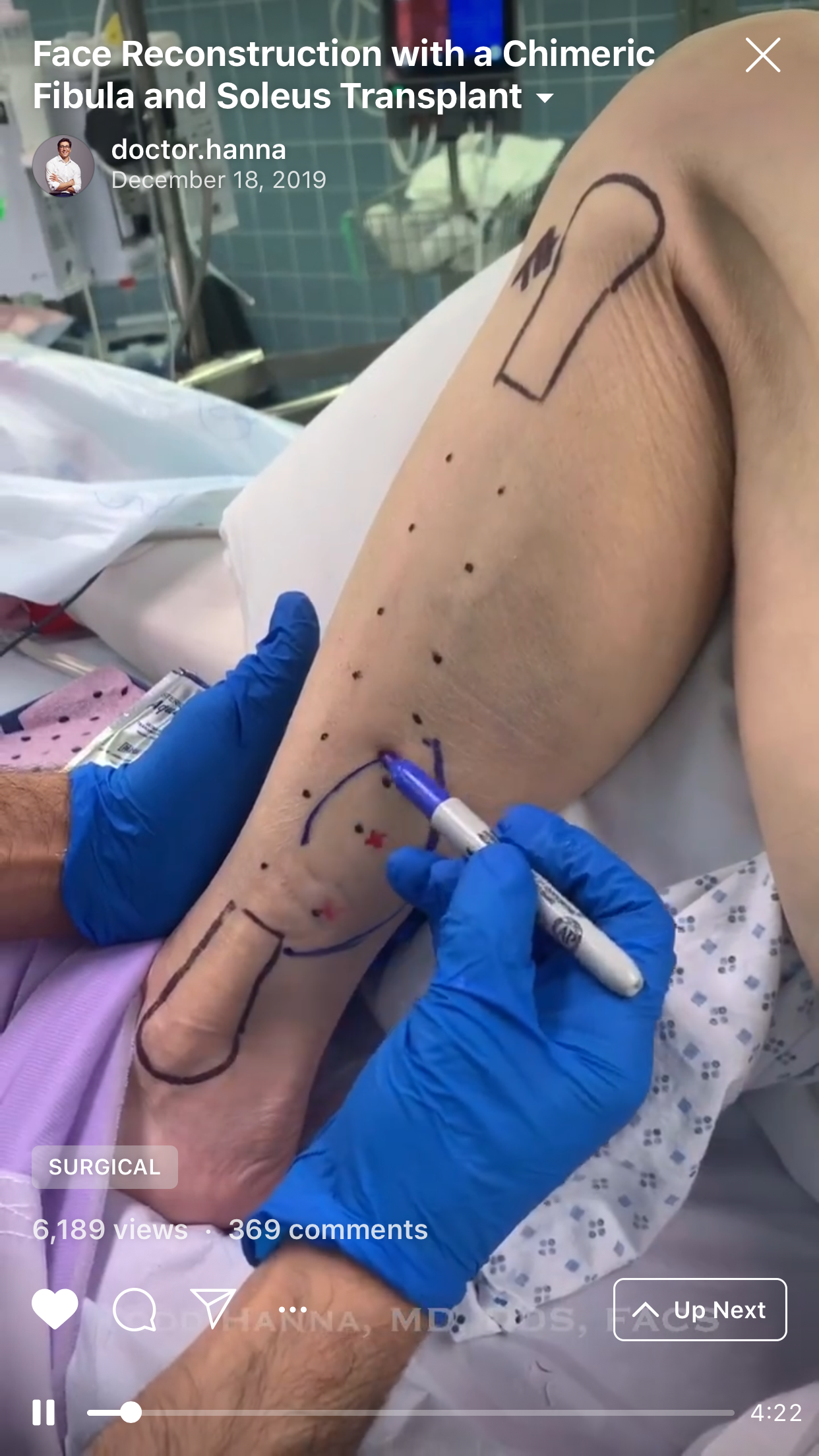
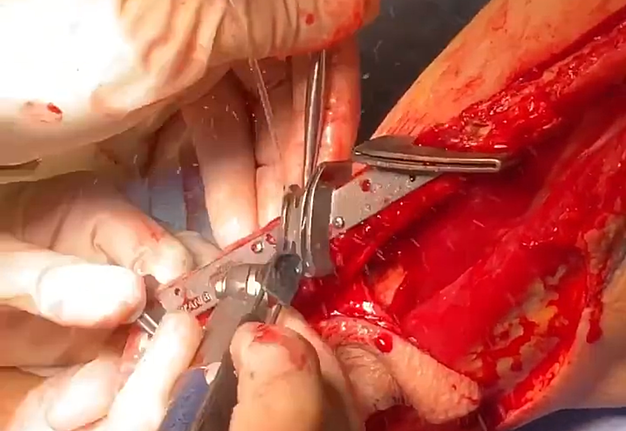
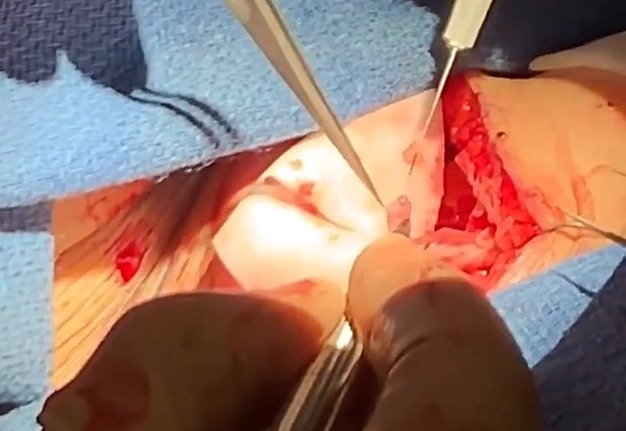
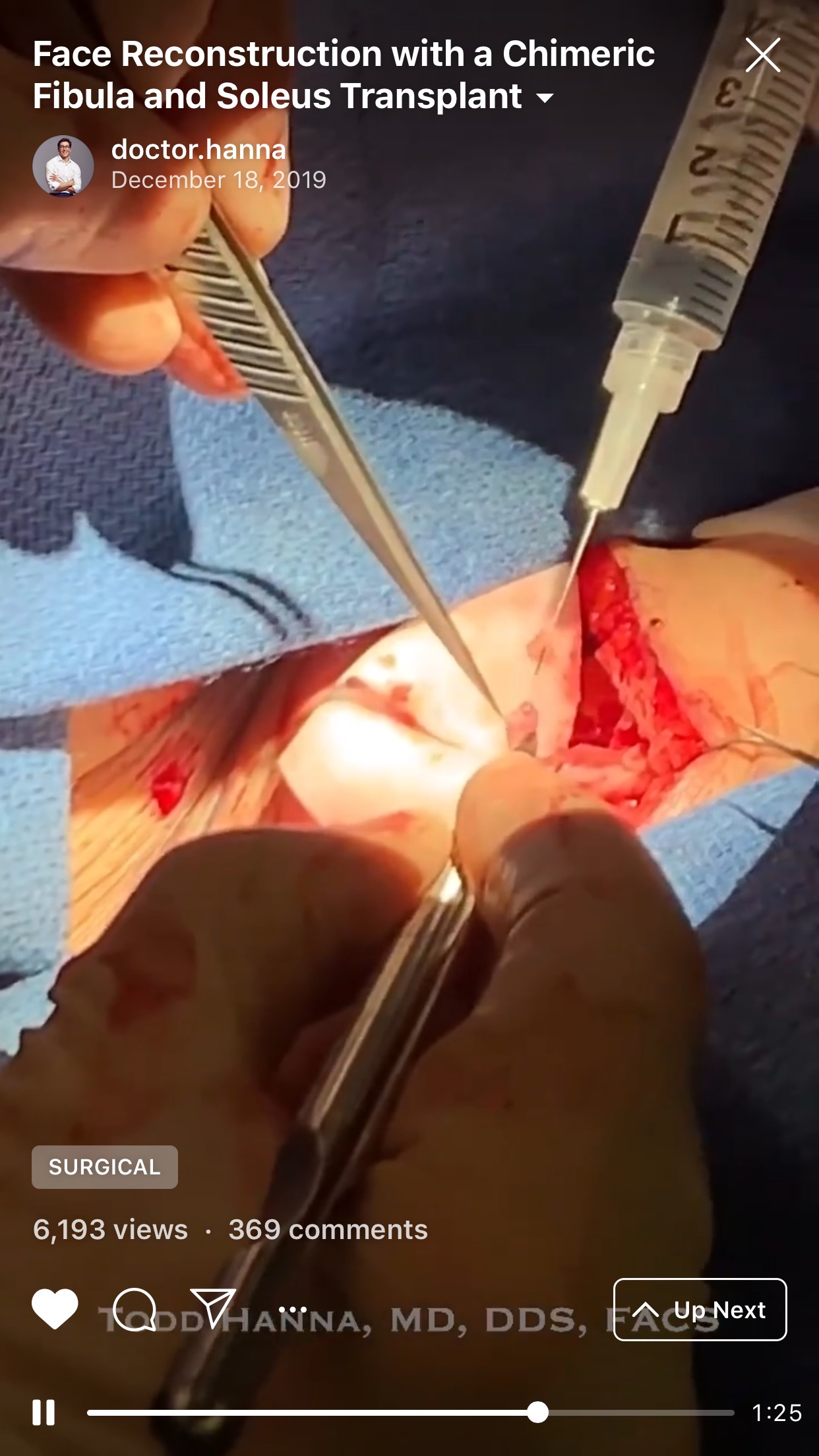
1. “Chapter 1: The harvest” (Fig 1).
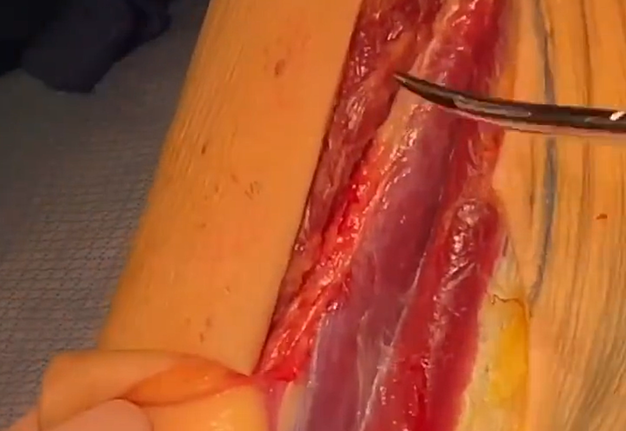
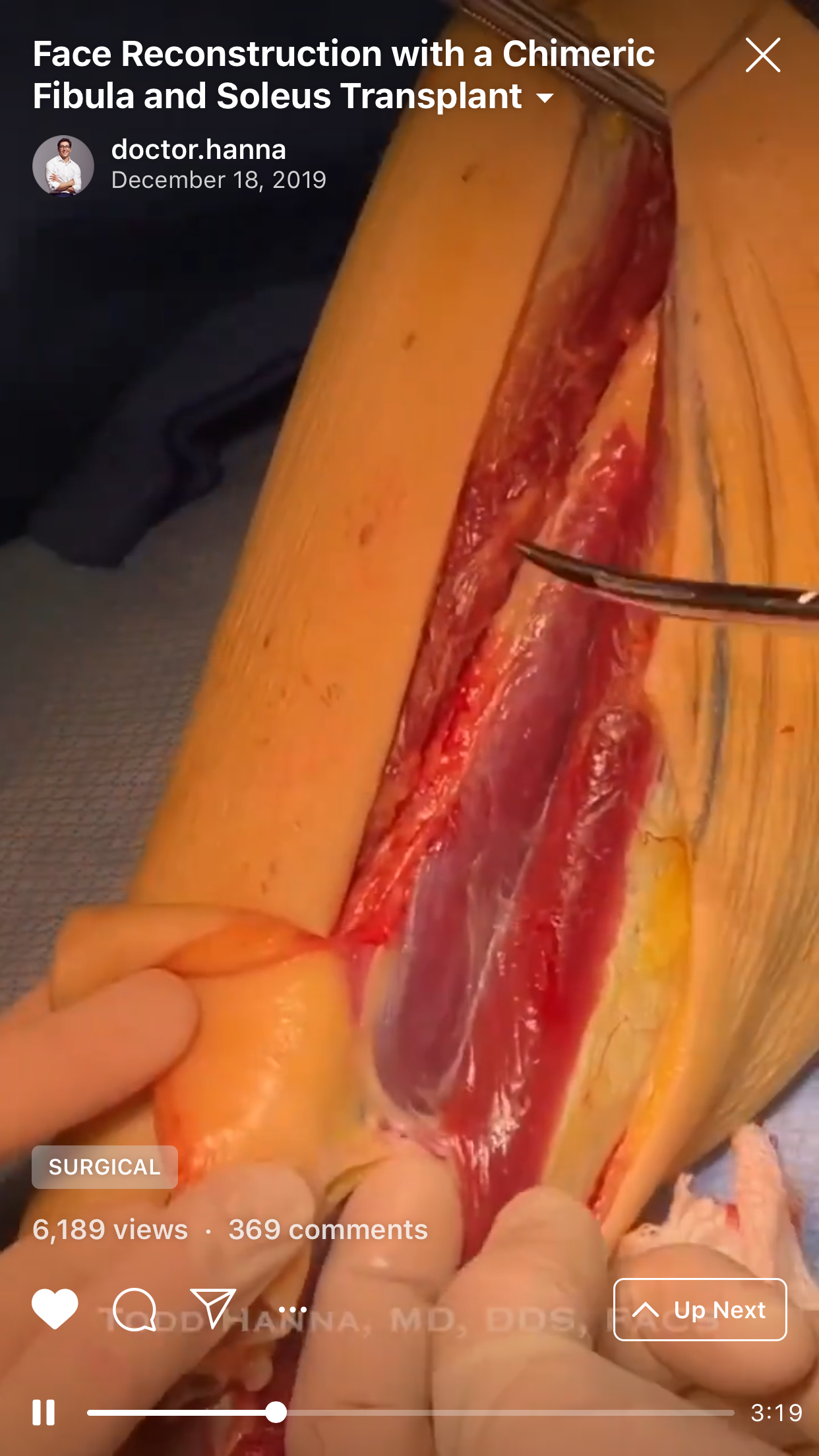
2. “Chapter 2: The soleus chimera” (Fig 2).
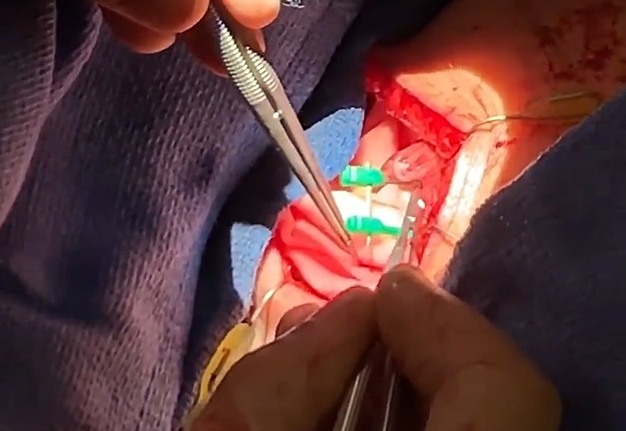
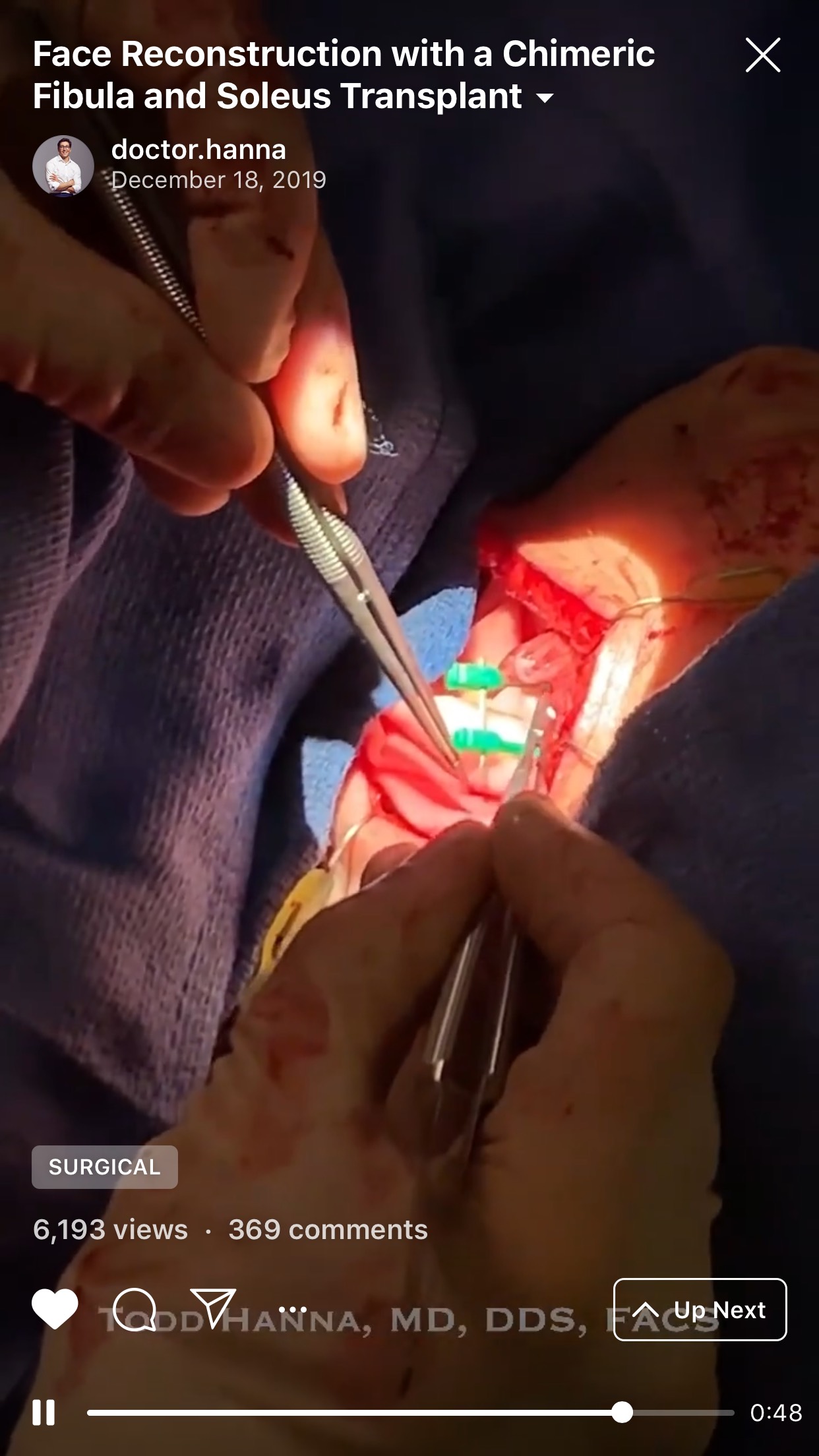
3. “Chapter 3: The osteotomies” (Fig 3).
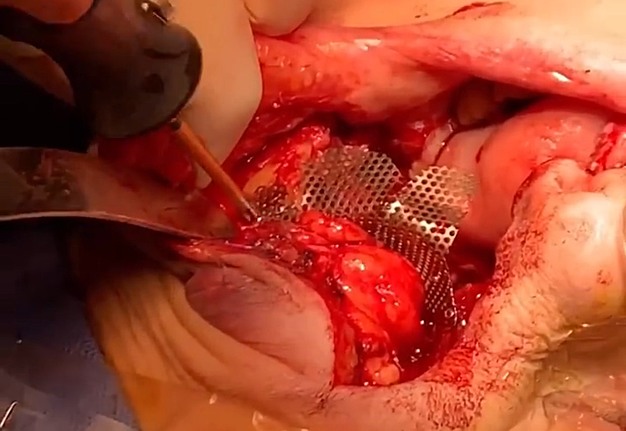
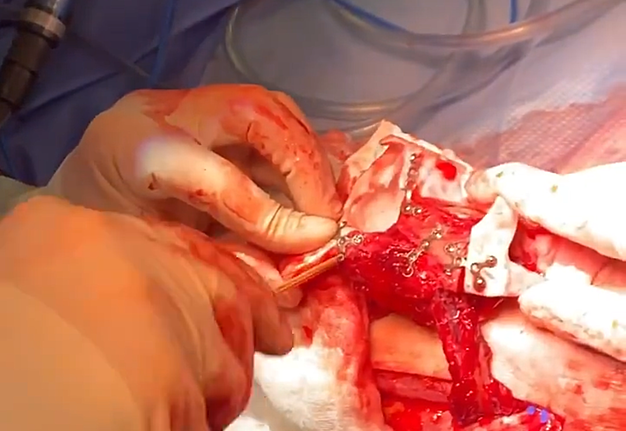
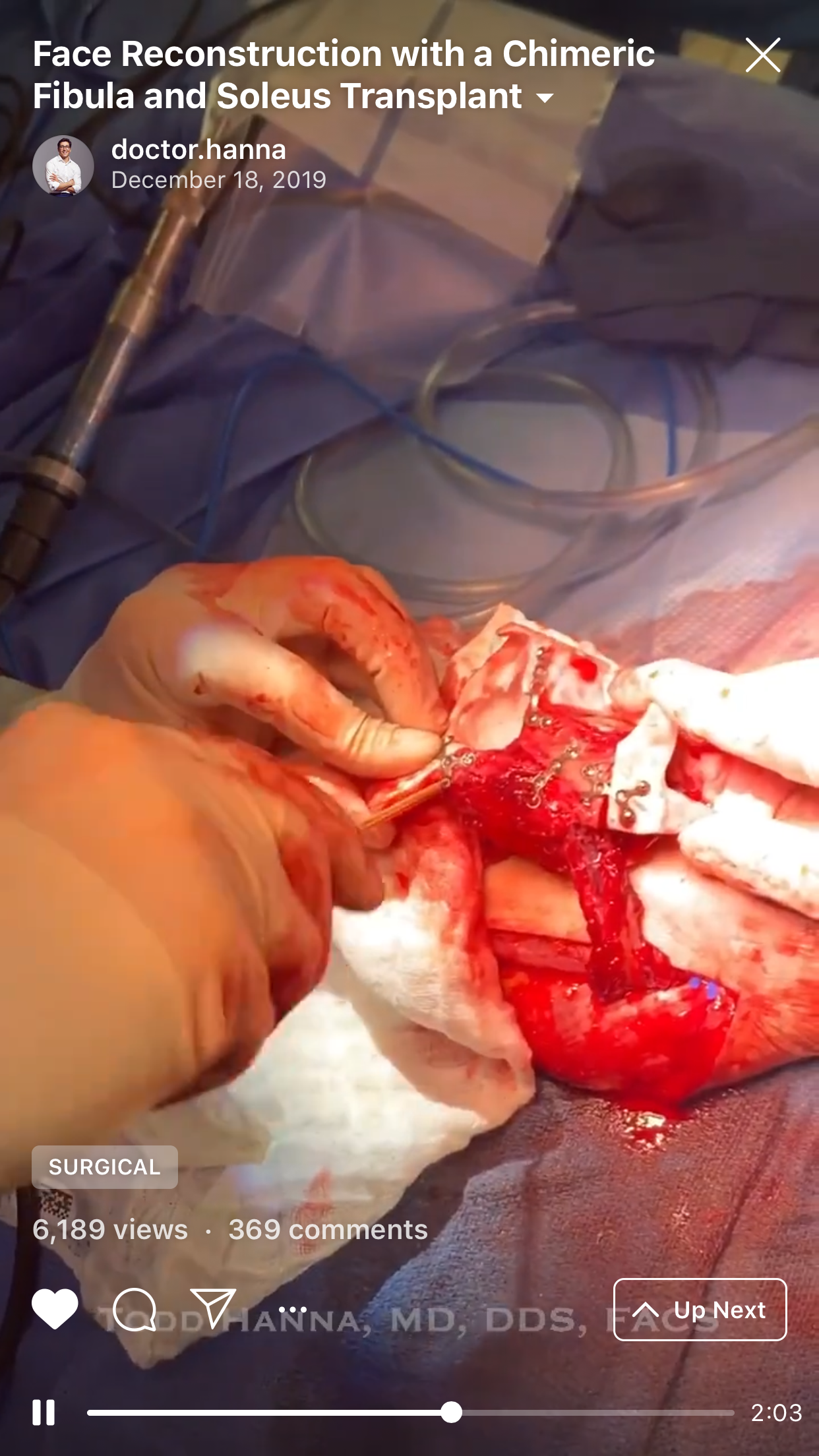
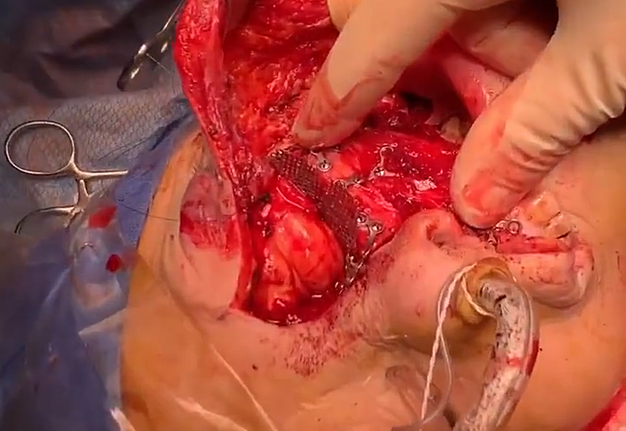
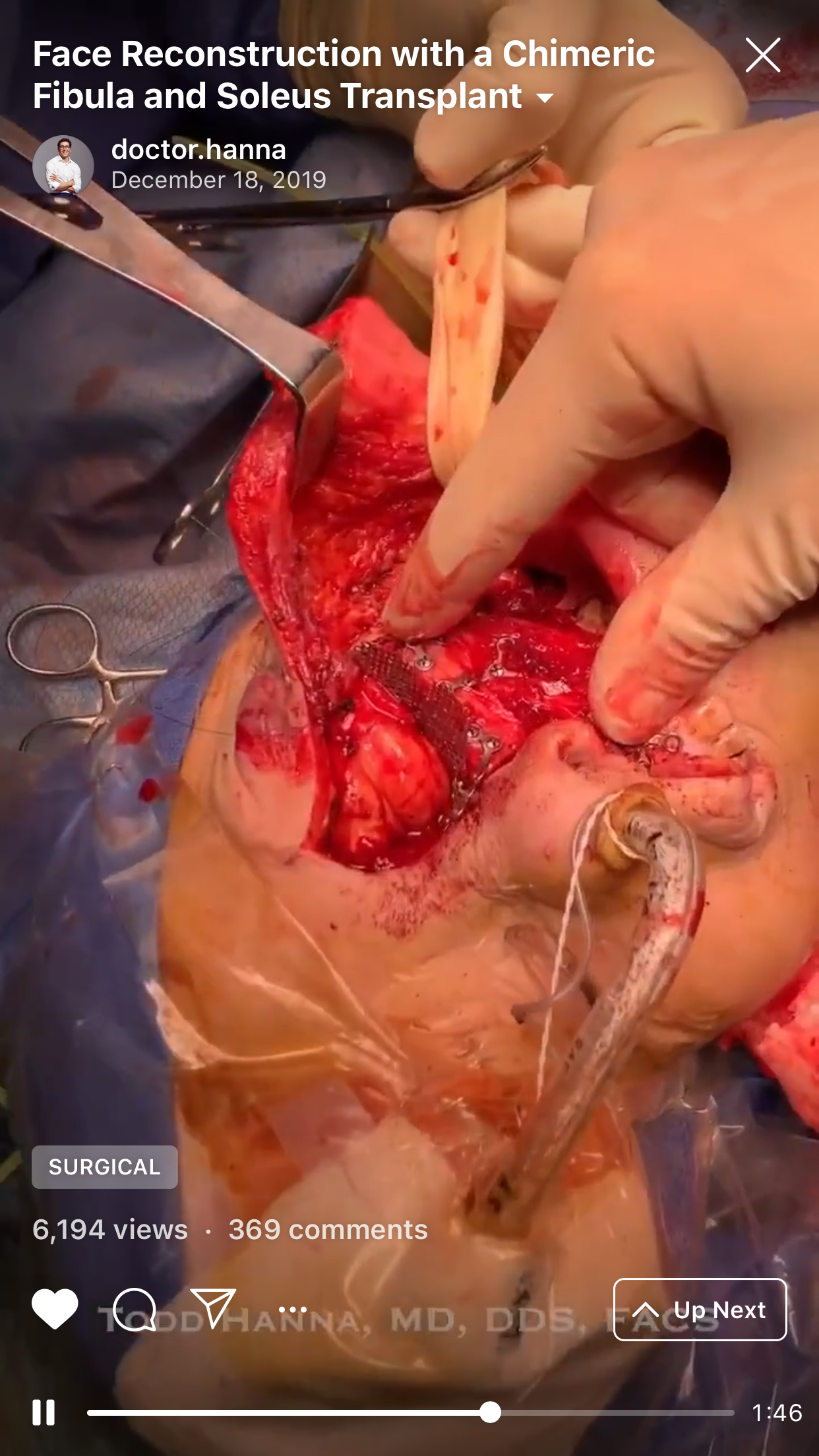
4. “Chapter 4: Orbital mesh. The conformation” (Fig 4).
5. “Chapter 5: Model inset. The template” (Fig 5).
6. “Chapter 6: Facial inset. The transference” (Fig 6).
7. “Chapter 7: Vessel preparation. Bring in the scope” (Fig 7).
8. “Chapter 8: The microvascular anastomosis. Slow is smooth, smooth is fast” (Fig 8).
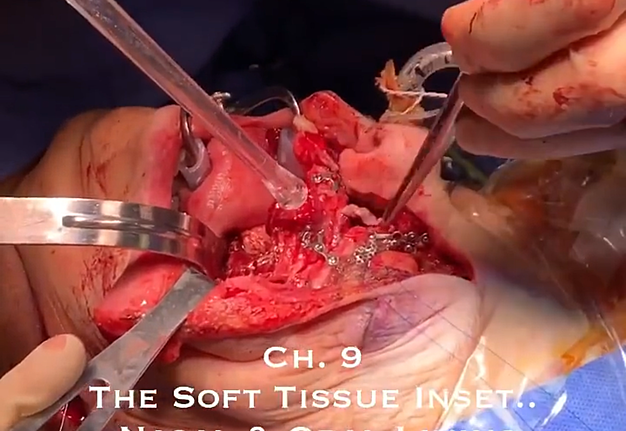
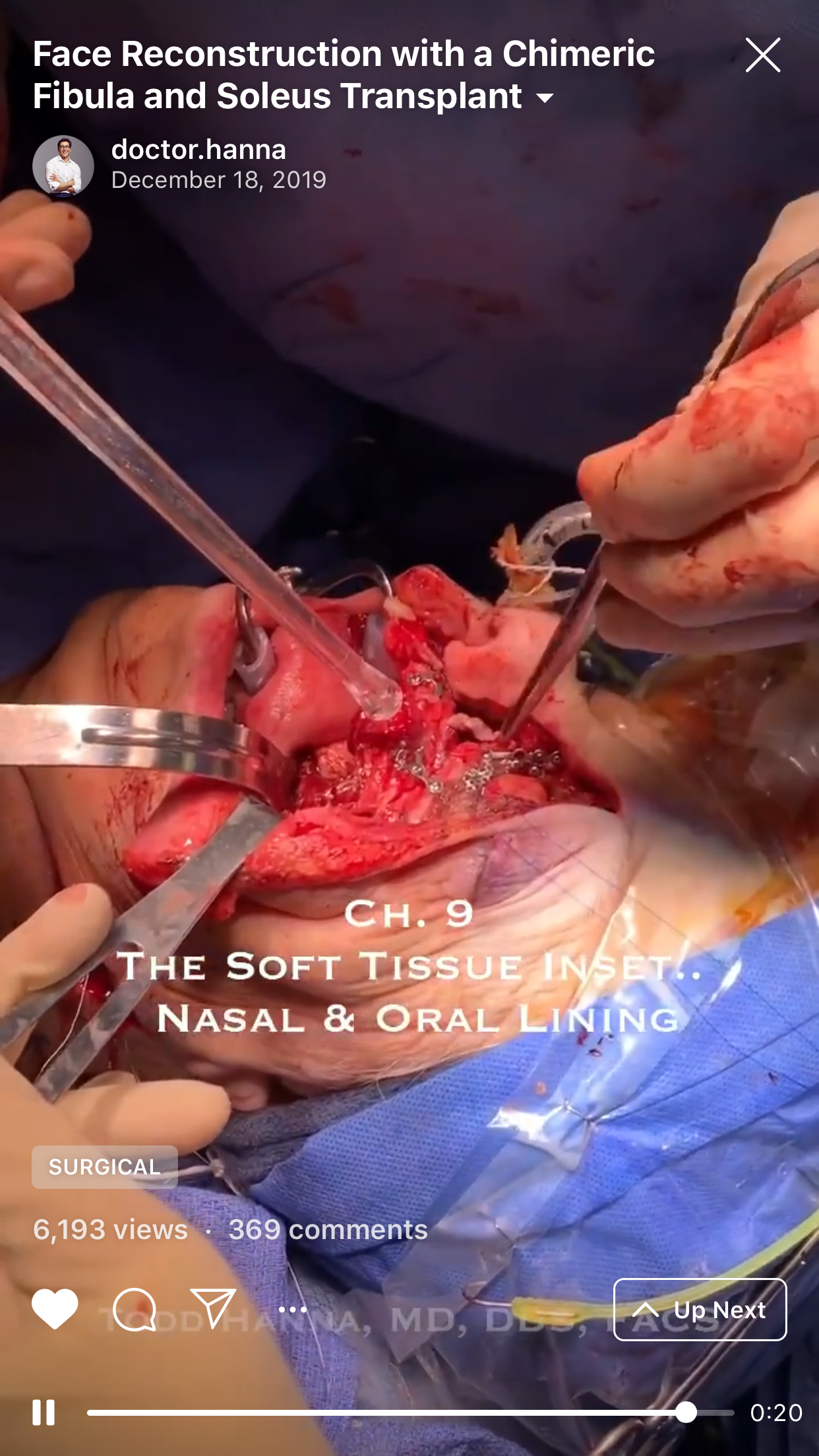
9. “Chapter 9: The soft tissue inset. Nasal and oral lining” (Fig 9).
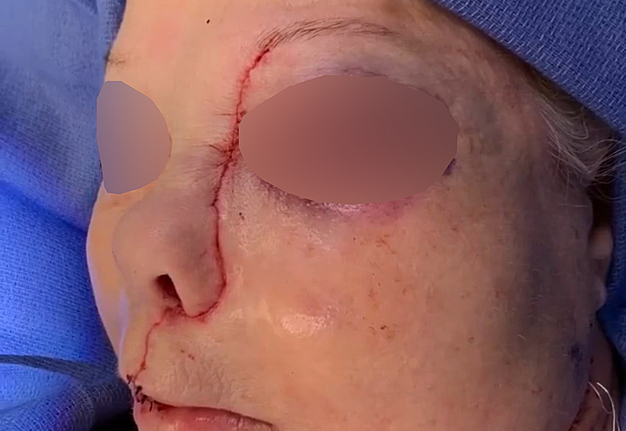
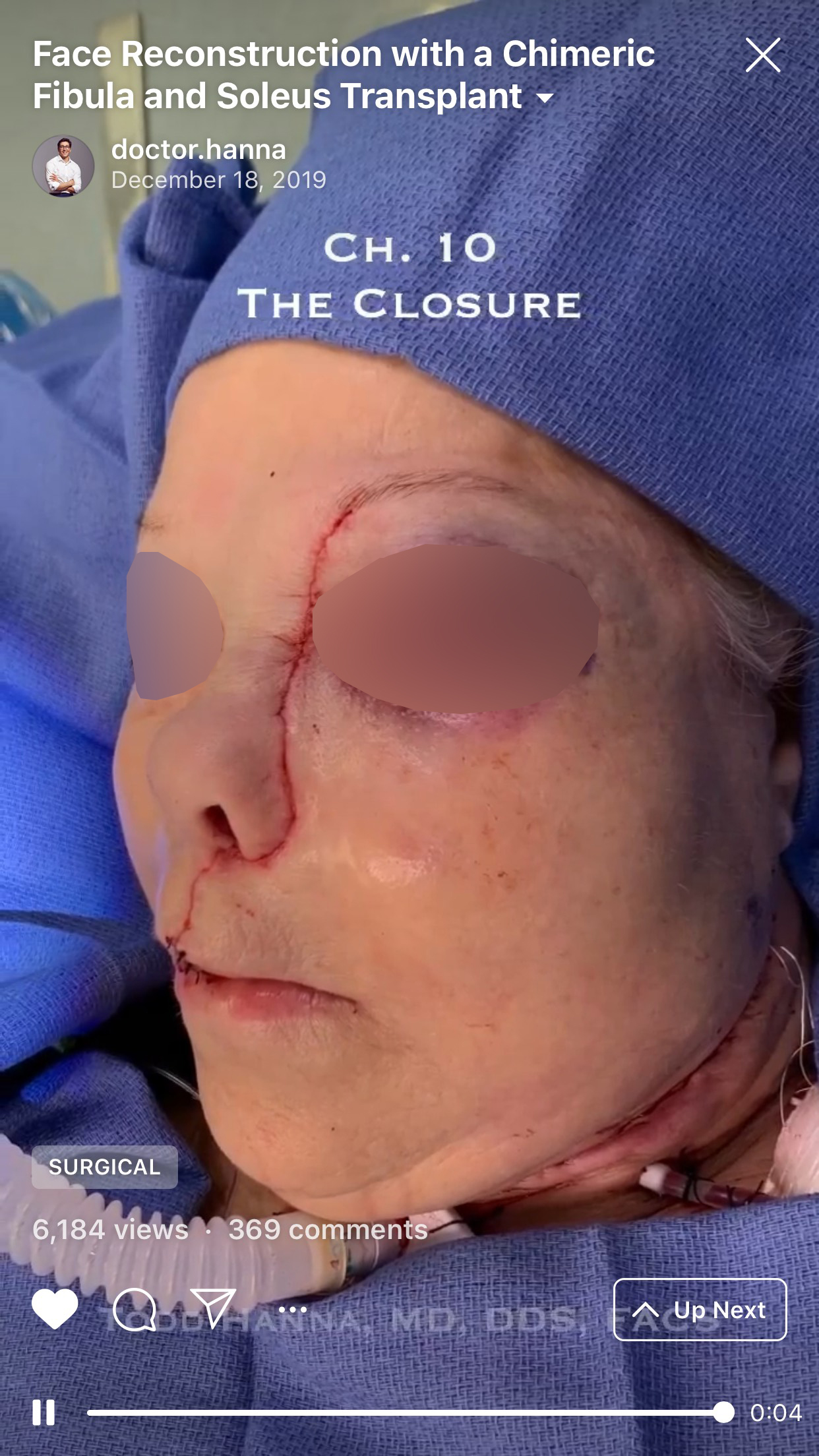
10. “Chapter 10: The closure” (Fig 10).
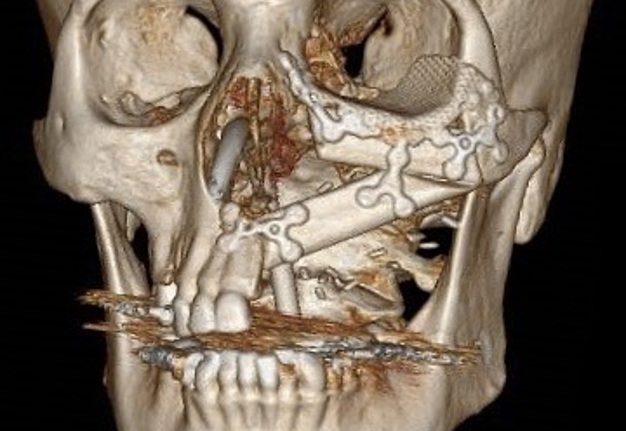
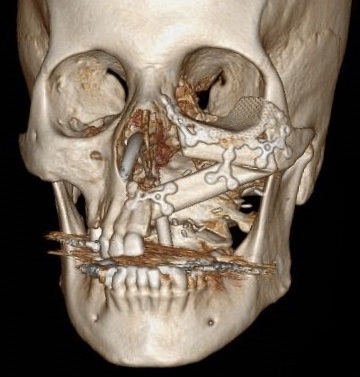
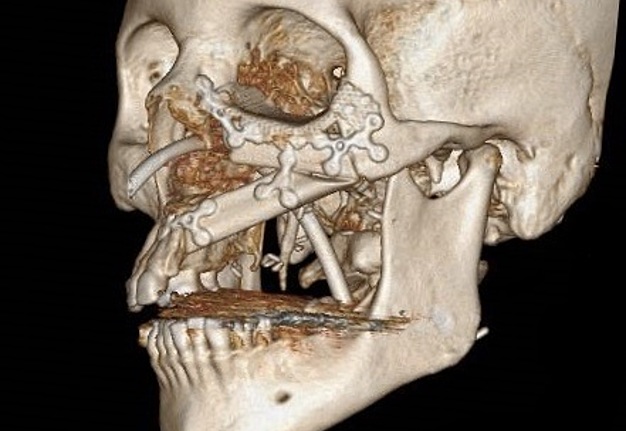
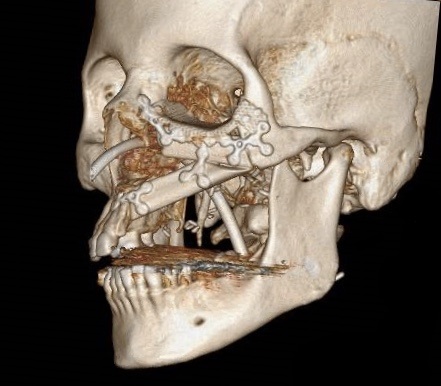
The aim of this chimeric flap case was to reconstruct Cordeiro type IIIA total left maxillectomy defect (after squamous cell carcinoma removal) including the floor of the orbit but sparing the orbital contents.14 Type IIIA defect reconstruction included usage of titanium orbital mesh, one L shape, and three Х shape mini plates. Virtual surgical planning provided precise position of the osseous components of the chimeric transplant what was noted on postoperative three-dimensional computed tomography (Fig 11). Dental implantation (one zygomatic implant and one anterior implant with bicortical placement) was planned to be performed secondary.
FIGURE 11A. Post-operative three-dimensional computed tomography. Notes precise position of the osseous components of the chimeric transplant after reconstruction of Cordeiro type IIIA total left maxillectomy defect using virtual surgical planning. Printed with permission and copyrights retained by T.C.H.
FIGURE 11B. Post-operative three-dimensional computed tomography. Notes precise position of the osseous components of the chimeric transplant after reconstruction of Cordeiro type IIIA total left maxillectomy defect using virtual surgical planning. Printed with permission and copyrights retained by T.C.H.
IGTV STATISTICS OF THE CASE
Analysis of the number of views, comments, and followers after publication the IGTV video case dedicated to microvascular surgery in a surgeon`s Instagram account during first 3 weeks is presented in Table 1. From our standpoint the impact of IGTV surgical video can be measured by:
1. Number of views.
2. Number of comments.
3. Number of new connections between surgeons.
4. Number of new collaborations related with published topic between specialists who are involved into 1) surgical education/training (finished fellowship programs on the base of the opinion leader`s [IGTV account holder] medical institution) or 2) surgeries alone.
Discussion
According to Buntic and Bunke the chimeric flap is a flap which is composed of more than one flap each on its own pedicle but with both on a common source pedicle.15 Despite the myriad of combinations15 of the chimeric flaps which can be created there are some most popular examples16 in the reconstruction of composite head and neck defects6.
Ettyreddy et al16 analyzed 521 chimeric flaps in the reconstruction of head and neck defects. The leading flap became a chimeric anterolateral thigh flap (N = 213 flaps, i.e. 40.88 percent of flaps), second most popular was subscapular flap (N = 141, i.e. 27.06 percent of flaps), in 16.21 percent of flap cases were chimeric fibulas, 13.24% reached the number of chimeric anterior tibial flap with dorsalis pedis skin paddle.16 According to their study less than 1% scored such chimeric flaps as rectus abdominis free flap, chimeric groin flap with multiple skin paddles, and a chimeric radial forearm free flap.16
Upon maxillary reconstruction after oncological surgical defect appears a need to use free flaps with osseous components. And some variations of chimeric fibula perfectly match those requirements:
- Gullwing fibula osteofascial flap and flexor hallucis longus muscle17 successfully face the challenges of the Cordeiro type II maxillary defects.
- The composite fibula and soleus free transfer for Cordeiro type III total maxillectomy defects.18, 19
- Chimeric lateral supramalleolar artery perforator fibula free flap6, 20, 21 for 1) Cordeiro type IIB, as sandwich flap despite of radial osteocutaneous sandwich flap, and 2) type IV when you want to achieve a prosthetic correction of postenucleation socket syndrome (synonym: post-enucleation/evisceration socket syndrome)22, 23 and you don`t want to fill the orbital cavity.
Nokovitch et al19 emphasized that first description of the fibula flap including the lateral head of the soleus muscle was presented by Baudet et al18 in 1982. Nokovitch with colleagues clearly described that composite fibula and soleus free transfer serve for better functional and aesthetic outcomes.19 As it not only restores osseous defect but also obliterates the dead space.19 Results of Ettinger et al24 proved that chimeric osteomusculocutaneous fibular flap with soleus muscle and skin paddle components can be successfully implemented also in cases of complex ablative defects resulting from advanced-staged the floor of mouth squamous cell carcinomas.
DENTAL IMPLANTS INTO CHIMERIC FLAPS
Comparing four osteocutaneous flaps (fibula, scapula, iliac crest, and radius), Lin et al25 indicated that fibula and iliac crest free flaps have the best characteristics for the dental implantation.
Massarelli et al reported a second ever published results dedicated to chimeric lateral supramalleolar artery perforator fibula free flap for composite head and neck defects, and presented as well their experience of secondary dental implantation into osseous portion of chimeric flap in the reconstruction of mandibular defects.6 Two of 10 chimeric-flap mandibles received 10 implants, with 5 implants for each reconstructed mandible.6 Ten osseointegrated implants with 43-month and 23-month follow-up showed no lost.6
POSSIBILITIES OF IGTV
Comparison of videos` duration in Instagram and IGTV is presented in Table 2. Despite official Instagram, Inc. page does not mention26 the restrictions on posting IGTV videos with different duration for average users and users with “more followers,” a lot of sources indicates that the difference does exist (Table 2).3, 27
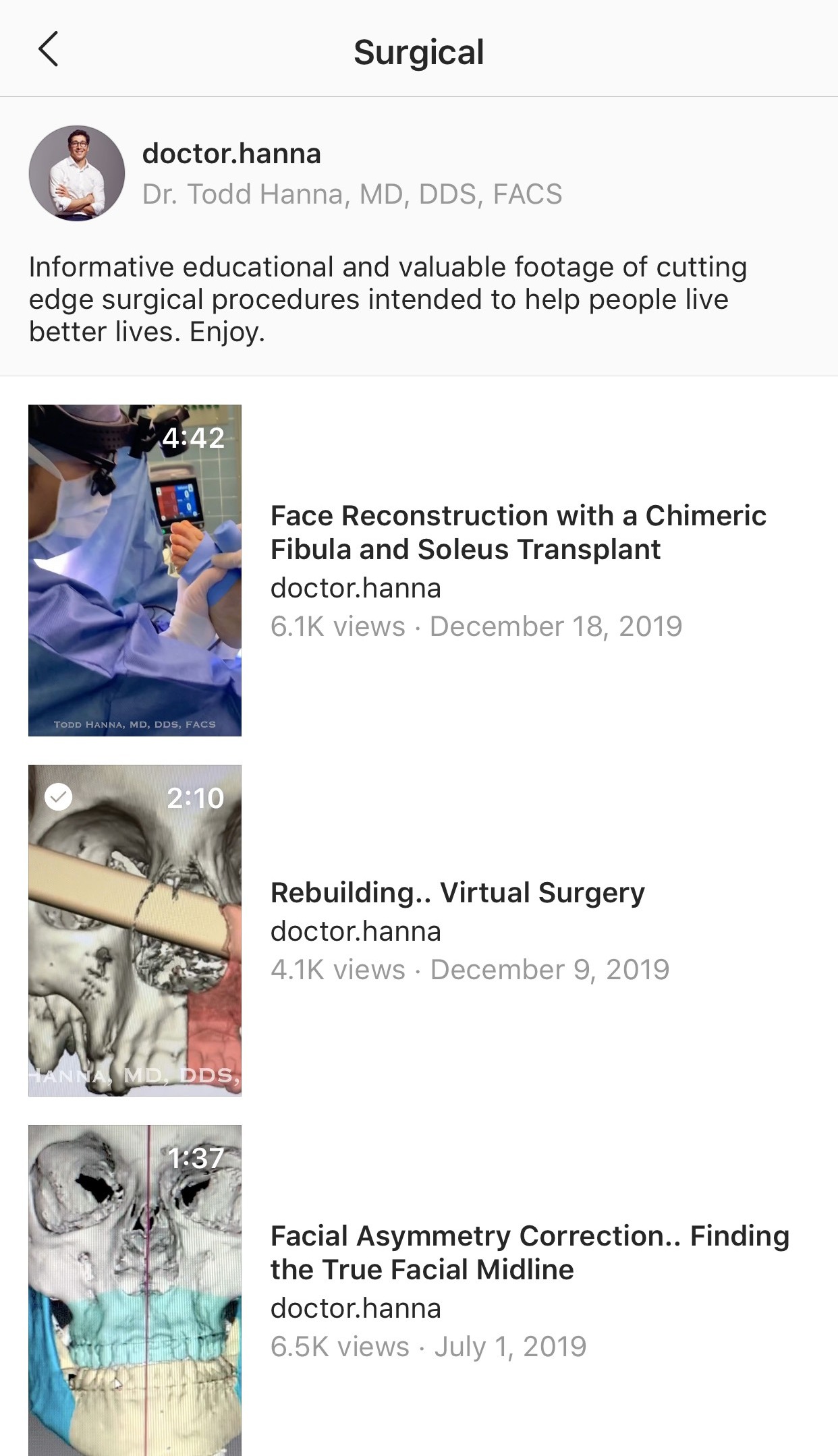
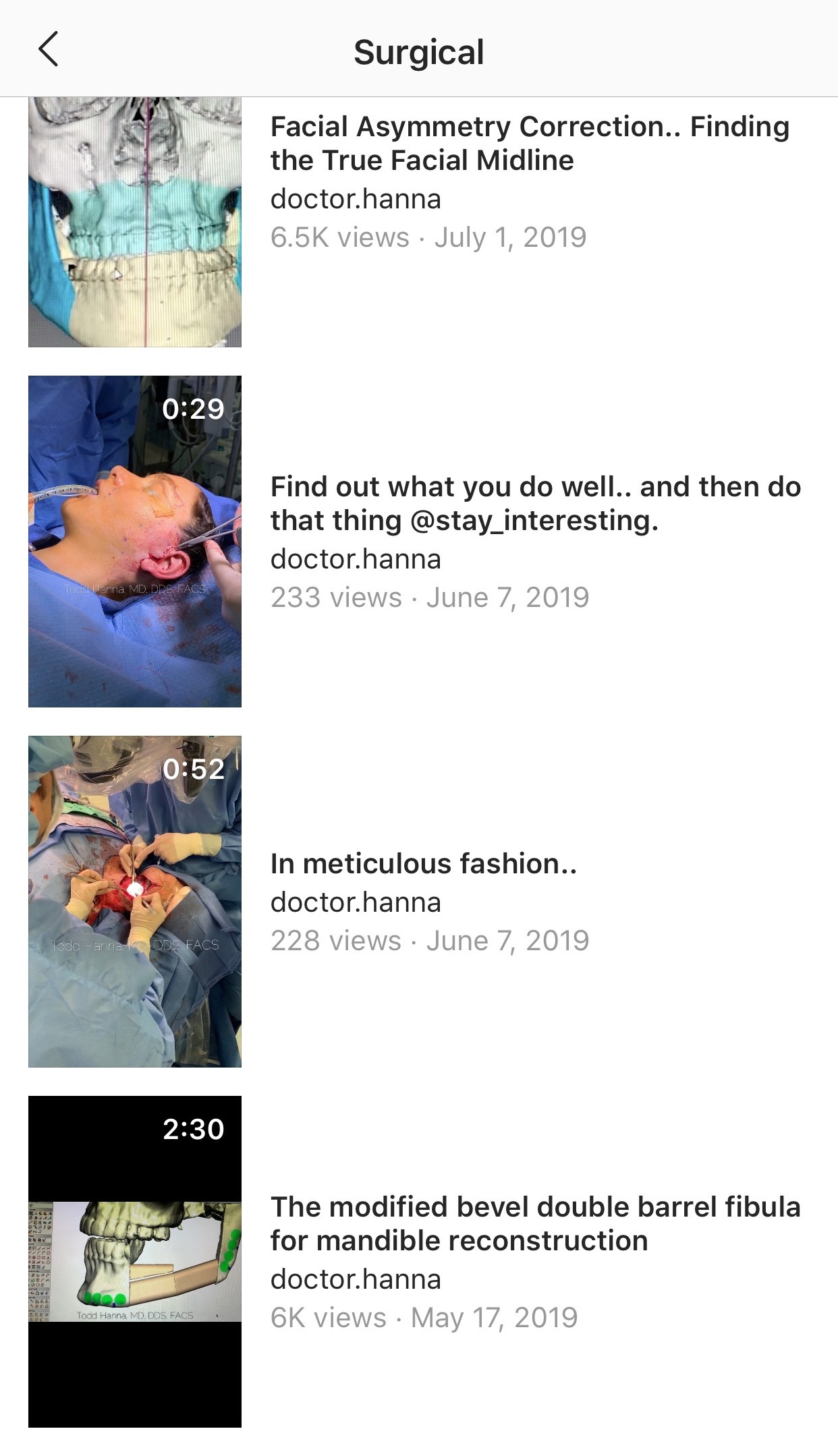
Window which is opened on smartphone screen after clicking on the button “SURGICAL,” which is visualized upon watching Dr. Hanna`s IGTV videos (Fig 12), shows: 1) short description of the topic “Surgical” and 2) list of all video cases published by the surgeon under that topic with indicated videos` titles, duration, amount of views, and the dates of publication.
FIGURE 12A. Window (A, B) which is opened on smartphone screens after clicking on the button “SURGICAL” shows:
1. Short description of the topic “Surgical.”
2. List of all video cases published by the surgeon under that topic with indicated videos` titles, duration, amount of views, and the dates of publication. Printed with permission and copyrights retained by T.C.H.
FIGURE 12B. Window (A, B) which is opened on smartphone screens after clicking on the button “SURGICAL” shows:
1. Short description of the topic “Surgical.”
2. List of all video cases published by the surgeon under that topic with indicated videos` titles, duration, amount of views, and the dates of publication. Printed with permission and copyrights retained by T.C.H.
CONCLUSIONS
We remember the words mentioned in one of the editorials` published by Dr. Rod J. Rohrich, editor-in-chief of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, “one picture can be worth 1000 words.”28 And after analysis of this IGTV video chimeric flap case we can affirmatively say that one surgical video with an academic educational approach can be worth 1000 pictures.
If you focus on producing a great experience for anyone, that's how you get big.
—Kevin Systrom
Former CEO of Instagram
Patient Consent
The patient provided written consent of the use of her images.
References (28)
- Monteiro JL, Fesenko II. Every hashtag matters: an importance of that Instagram tool in a life of the peer-reviewed journal. J Diagn Treat Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2019;3:A11. Crossref | Google Scholar
- Parsons J. What is Instagram IGTV and how do you use it effectively? [document on the internet]; October 18, 2018 [cited 2020 Jan 2]. Available from: Link
- Belanger L. Everything you need to know about IGTV, Instagram's new longform video app. [document on the internet]; June 20, 2018 [cited 2020 Jan 2]. Available from: Link
- Daya M. Peroneal artery perforator chimeric flap: changing the perspective in free fibula flap use in complex oromandibular reconstruction. J Reconstr Microsurg 2008;24:413–8. Crossref | Medline | Google Scholar
- Roan TL, Chen CC, Yu YC, Hsieh JH, Horng SY, Tai HC, Cheng NC, Chien HF, Tang YB. A modified free chimeric osteocutaneous fibular flap design for head and neck reconstruction: experience on a series of 10 cases. Microsurgery 2013;33:439–46. Crossref | Medline | Google Scholar
- Massarelli O, Gobbi R, Biglio A, Soma D, Tullio A. Chimeric lateral supramalleolar artery perforator fibula free flap in the reconstruction of composite head and neck defects. Plast Reconstr Surg 2014;133:130–6. Crossref | Medline | Google Scholar
- Fernandes RP, Quimby A, Salman S. Comprehensive reconstruction of mandibular defects with free fibula flaps and endosseous implants. J Diagn Treat Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2017;1:6−10. Crossref | Google Scholar
- Hanna TC, Kraus DH. State of the art simultaneous bilateral segmental mandibular reconstruction using a single fibula transplant: discussion of the surgical steps. J Diagn Treat Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2019;3:76−103. Crossref | Google Scholar
- Qaisi M, Kolodney H, Swedenburg G, Chandran R, Caloss R. Fibula jaw in a day: state of the art in maxillofacial reconstruction. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2016;74:1284.e1−1284.e15. Crossref | Medline | Google Scholar
- Kuo YR, Shih HS, Chen CC, Boca R, Hsu YC, Su CY, Jeng SF, Wei FC. Free fibula osteocutaneous flap with soleus muscle as a chimeric flap for reconstructing mandibular segmental defect after oral cancer ablation. Ann Plast Surg 2010;64:738−42. Crossref | Medline | Google Scholar
- Huang YC, Leong CP, Pong YP, Liu TY, Kuo YR. Functional assessment of donor-site morbidity after harvest of a fibula chimeric flap with a sheet of soleus muscle for mandibular composite defect
reconstruction. Microsurgery 2012;32:20−5. Crossref | Medline | Google Scholar - Ganry L, Sigaux N, Ettinger KS, Salman SO, Fernandes RP. Modified GoPro Hero 6 and 7 for intraoperative surgical recording-transformation into a surgeon-perspective professional quality recording system. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2019;77:1703.e1–1703. Crossref | Medline | Google Scholar
- Tymofieiev OO, Fesenko II, Monteiro JL. DTJournal: Instagram stories metrics. J Diagn Treat Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2019;3:A11. Crossref
- Cordeiro PG. Classification system for maxillectomy defects. In: De Santis G, Cordeiro PG, Chiarini L, editors. Atlas of mandibular and maxillary reconstruction with the fibula flap. Springer, 2019:7–9. Crossref | Google Scholar
- Buntic R, Bunke HJ. Principles of microvascular free tissue transfer. In: Weinzweig J, editor. Plastic surgery secrets plus. Elsevier Mosby 2010:712–6.
- Ettyreddy AR, Chen CL, Zenga J, Simon LE, Pipkorn P. Complications and outcomes of chimeric free flaps: a systematic review. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2019;161:568–75. Crossref | Medline | Google Scholar
- Mitchell SL, Seth AK, Matros E, Cordeiro PG. Maxillary reconstruction using a gullwing fibula osteofascial flap and flexor hallucis longus muscle. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 2018;6:e1821. Crossref | Medline | Google Scholar
- Baudet J, Panconi B, Caix P. The composite fibula and soleus free transfer. Int J Microsurg 1982;4:10.
- Nokovitch L, Davrou J, Bidault F, Devauchelle B, Dakpé S, Vacher C. Vascular anatomy of the free fibula flap including the lateral head of the soleus muscle applied to maxillo-mandibular reconstruction. Surg Radiol Anat 2019;41:447–54. Crossref | Medline | Google Scholar
- Sicilia-Castro D, Garcia-Perla A, Infante-Cossio P, GutierrezPerez JL, Gomez-Cia T, Garcia-Perla A. Combined fibula osteoseptocutaneous-lateral supramalleolar flap for reconstruction of composite mandibular defects. Plast Reconstr Surg 2003;111:2003–8. Crossref | Medline | Google Scholar
- Infante-Cossio P, Sicilia-Castro D, Garcia-Perla A, Gutierrez-Perez JL, Gomez-Cia T. Chimeric lateral supramalleolar artery perforator fibula free flap in the reconstruction of composite head and neck defects. Plast Reconstr Surg 2014;134:329e–331e. Crossref | Medline
- Camezind P, Robert PY, Adenis JP. Post-enucleation or evisceration socket syndrome. Operative Techniques in Oculoplastic, Orbital and Reconstructive Surgery 2001;4:48–51. Crossref | Google Scholar
- Peralta RJ, Lelli GJ, Zoumalan C. Anophthalmic socket. In: Schmidt-Erfurth U, Kohnen T, editors. Encyclopedia of ophthalmology. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2013. Crossref
- Ettinger KS, Ganry L, Fernandes RP. Oral cavity cancer. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am 2019;31:13–29. Crossref | Medline | Google Scholar
- Lin PY, Lin KC, Jeng SF. Oromandibular reconstruction: the history, operative options and strategies, and our experience. ISRN Surg 2011;2011:824251. Crossref | Medline | Google Scholar
- What are the video upload requirements for IGTV? [document on the internet]; 2020 [cited 2020 Jan 2]. Available from: Link
- Drake A. How long can Instagram videos be? (Post, Story, Live, + IGTV) [document on the internet]; October 17, 2019 [cited 2020 Jan 2]. Available from: Link
- Rohrich RJ. Improving letters and viewpoints. Plast Reconstr Surg 2005;115:1201. Crossref