Hemolymphangioma of the Neck
August 31, 2022
J Diagn Treat Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2022;6: 114–6.
Under a Creative Commons license
HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE
Demidov VH, Cherniak OS. Hemolymphangioma of the neck. J Diagn Treat Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2022;6(8):114–6. https://doi.org/10.23999/j.dtomp.2022.8.2
NATIONAL REPOSITORY OF ACADEMIC TEXTS
https://nrat.ukrintei.ua/en/searchdoc/2022U000192/
ARTICLE
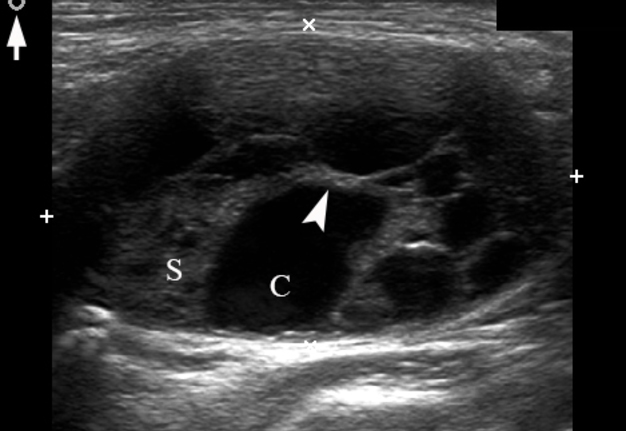
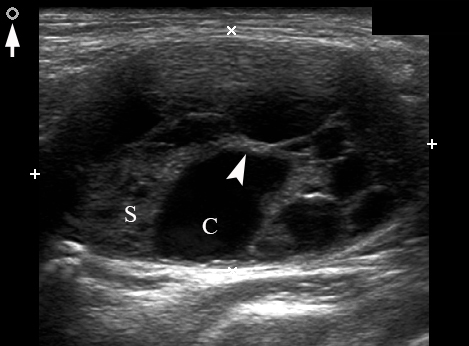
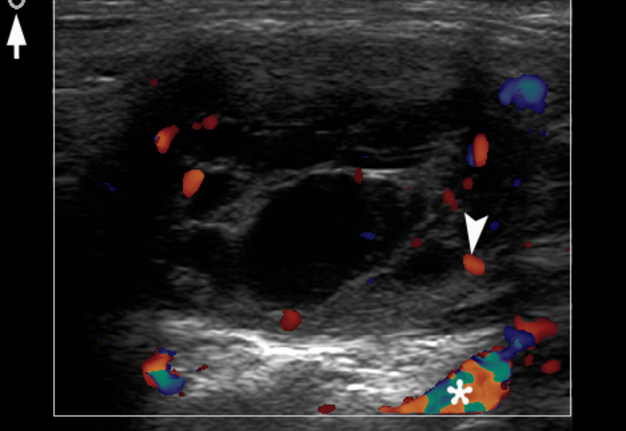
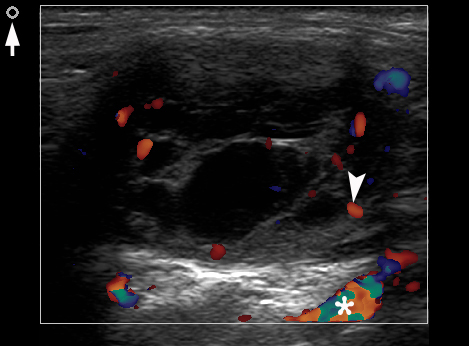
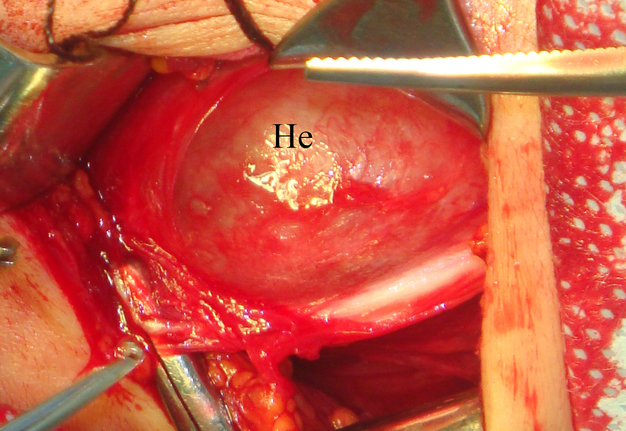
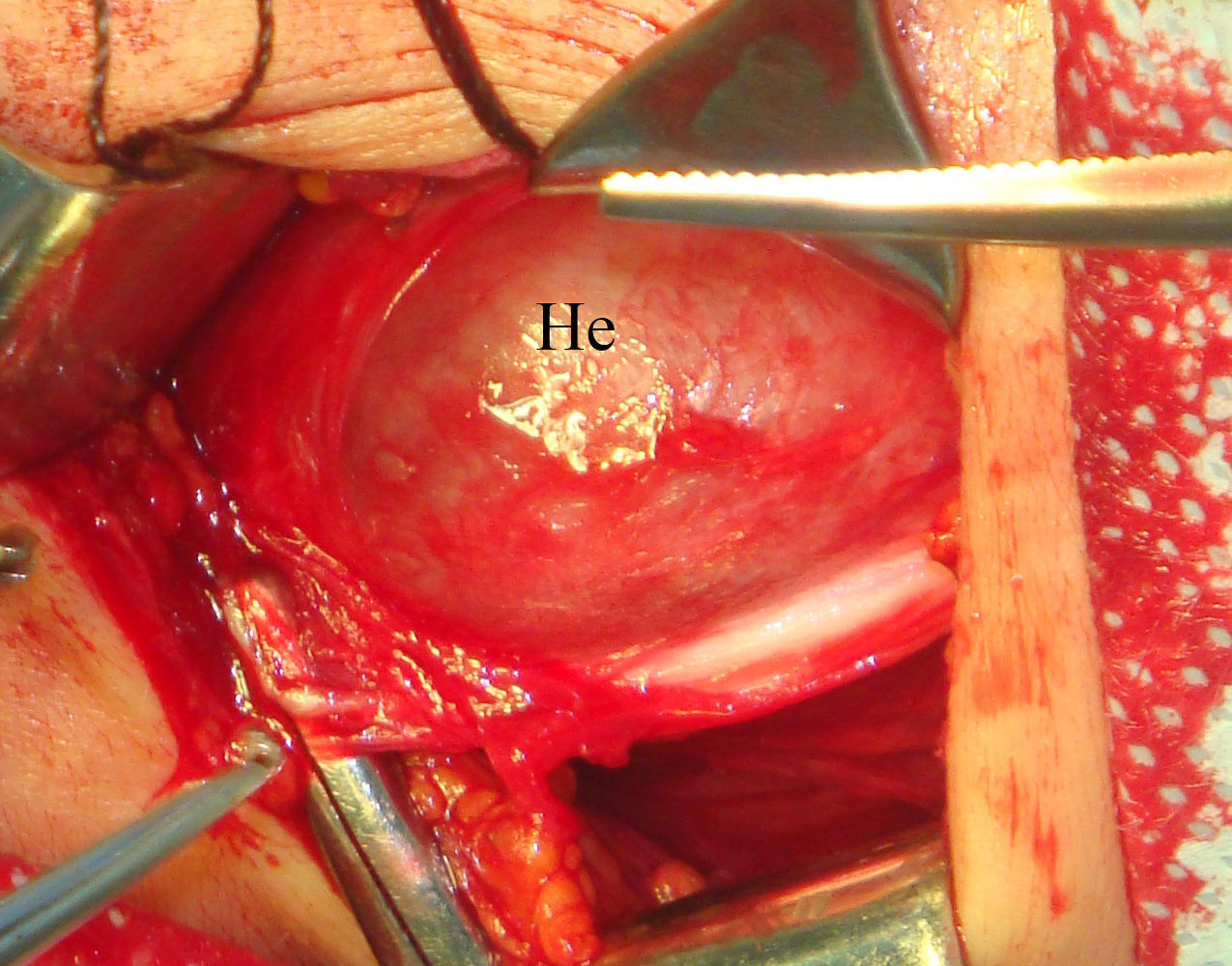
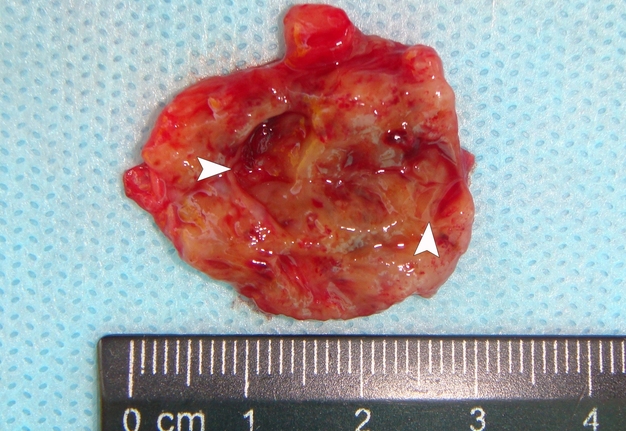
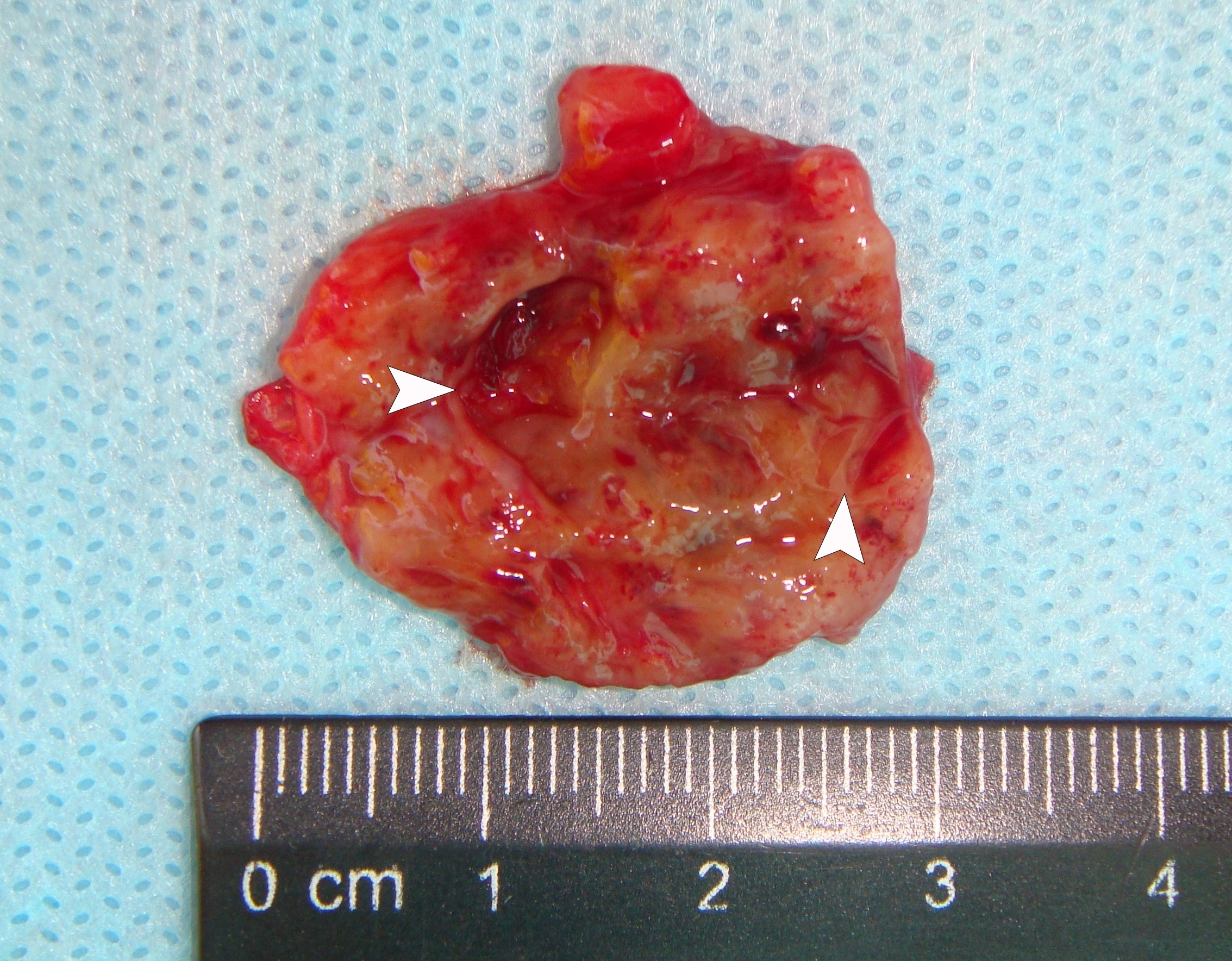
A 26-year-old female patient presented with a painless soft tissue mass at the lower third of the right neck. The mass appearance and growth was noted during last several years. Longitudinal gray-scale ultrasound (US) showed that long-to-short diameter of this cystic lesion measured 3.51 × 2.12 cm (distances are indicated by even calipers ‘+’ and ‘×’) (Panel A: arrow, position of the probe’s side which corresponds to the probe bump and symbolizes the probe side [arrow] at Panel C; arrowhead, septa; C, cystic component; S, solid component). Lesion is visualized as a multicystic mass (hypoechoic with multiple anechoic areas) with septations and a prominent mixed structure (combination of macro- and microcystic cavities). A honeycomb US pattern1 and no vascular fill of the anechoic areas (Panel B: arrow, position of the probe’s side; asterisk, neck vessel; arrowhead, weak intratumoral blood flow), most likely represented a lymphangioma2. Typically, the strong flow signal is noted from 9.30 to 59.37 percent of hemangioma cases.3,4 The artifact of acoustic enhancement―common for the fluid-containing structure―was noted posteriorly to the lesion. The fact that the tumor cannot be compressed using probe indicates that the cystic structure differs from the cystic structure of reported US features of cavernous lymphangiomas (sponge-like neoplasms)5. The capsulated lesion (Panel D: He, hemolymphangioma) was surgically removed under general anesthesia applying the incision along the anterior margin of the right sternocleidomastoid muscle. During tumor removal, light-gray fluid content was partially evacuated due to the rupture of cystic wall. Panel E shows a specimen―the decreased in volume mass―after the evacuation of its cystic content. The spaces of the intratumoral macrocysts are indicated by arrowheads. Histopathological examination established the diagnosis of a ‘hemolymphangioma’ (also known as ‘hemangiolymphangioma’6,7). The patient showed no signs of recurrence at the end of the 36-month follow-up period. Li et al (2017) emphasized that it’s crucial to perform such preoperative imaging, which can help to avoid biopsy upon differential diagnostics between lymphangiomas and vascular malformations with numerous vessels (which can lead to intensive bleeding).8 In summary, hemolymphangioma is a very rare mixed malformation of both blood and lymphatic vessels.9 Ohsawa et al (2018) concluded that complete excision of hemolymphangiomas provides the best results with a lower recurrence rate.10 Diagnostic ultrasound and its Doppler option proved efficacy in case of such malformations. ■ DTJournal.org
REFERENCES (10)
- Martín-Pérez E, Tejedor D, Brime R, Larrañaga E. Cystic lymphangioma of the lesser omentum in an adult. Am J Surg 2010;199(2):e20–2. Crossref
- Khaunte DDN, Kumar PS, Dhupar V, Naik M. Hemangiolymphangioma of buccal cheek- a rare case report with review of literature. J Dent Health Oral Disord Ther 2020;11(5):150–4. Crossref
- Keng CY, Lan HHC, Chen CCC,Gueng MK, Su YG, Lee SK. Soft tissue hemangiomas: high-resolution grayscale and color Doppler ultrasonographic features in 43 patients. J Med Ultrasound 2008;16(3):223–30. Crossref
- Rózylo-Kalinowska I, Brodzisz A, Gałkowska E, Rózylo TK, Wieczorek AP. Application of Doppler ultrasonography in congenital vascular lesions of the head and neck. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 2002;31(1):2–6. Crossref
- Tymofieiev OO, Fesenko II, Cherniak OS, Zaritska VI. Features of diagnostics, clinical course and treatment of the branchial cleft cysts. J Diagn Treat Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2017;1(1):15–31. Crossref
- Agüero ME, Rojas RGA, Islas DA. Cystic hemangiolymphangioma of the neck. Case report [in Spanish]. An Med Asoc Med Hosp ABC 2014;59(4):299–303.
- Manickam S, Sasikumar P, Kishore BN, Joy S. Hemangiolymphangioma of buccal mucosa: a rare case report. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2017;21(2):282–5. Crossref
- Li Y, Zhang X, Pang X, Yang L, Peng B. Occipitocervical hemolymphangioma in an adult with neck pain and stiffness: case report and literature review. Case Rep Med 2017;2017:7317289. Crossref
- Senoh D, Hanaoka U, Tanaka Y, Tanaka H, Hayashi K, Yanagihara T, Hata T. Antenatal ultrasonographic features of fetal giant hemangiolymphangioma. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2001;17(3):252–4. Crossref
- Ohsawa M, Kohashi T, Hihara J, Mukaida H, Kaneko M, Hirabayashi N. A rare case of retroperitoneal hemolymphangioma. Int J Surg Case Rep 2018;51:107–11. Crossref